With the Industrial Internet of Things fast becoming the norm in industries, converging IT and OT technologies securely—a cornerstone of the IIoT—is still the Achilles heel for many companies. Thus, choosing the right industrial connectivity and networking solution for your operation, and this cannot be repeated often enough, is essential. At the same time, this is easier said than done. Too often, this arduous task befalls an IT engineer with little experience of OT protocols and automation systems, or, on the flip side, an OT engineer with no knowledge of enterprise IT networking. In this article, we take a closer look at how new technologies are shaping the role of industrial connectivity and networking solutions in your IIoT applications.
Industrial Connectivity Needs—Now and in the Future
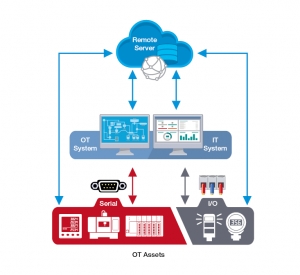
Connecting your previously unconnected industrial devices and assets is the first step to enabling IIoT applications. Accomplishing this task requires a thorough assessment of the types of OT assets you need to connect as well as the specific connectivity requirements, such as connecting OT assets to a local network or a cloud server. Since OT assets in industrial applications mainly use serial or I/O communication interfaces, choosing the right serial and I/O connectivity solutions is essential to enable industrial connectivity. Moreover, you need to keep in mind additional considerations, such as cybersecurity and large-scale device management, when connecting OT assets to remote or cloud servers.
 Serial Connectivity: As the vast majority of legacy machinery, equipment, and field devices still use a variety of standard and proprietary serial communication protocols, you may need a serial device server or protocol gateway in order for an Ethernet-based system to communicate with these legacy serial devices.
Serial Connectivity: As the vast majority of legacy machinery, equipment, and field devices still use a variety of standard and proprietary serial communication protocols, you may need a serial device server or protocol gateway in order for an Ethernet-based system to communicate with these legacy serial devices.
Remote I/O Connectivity: The role of remote I/O connectivity is no longer limited to simply collecting and transmitting digital or analog data. In IIoT applications, where both OT and IT systems need to acquire data from I/O devices, remote I/Os play an essential role in making data available to your application systems.
IIoT Device Connectivity: The connectivity devices you use to connect field devices in IIoT applications may also have additional requirements of their own. For example, connectivity devices may require IT protocols or cloud capabilities to communicate with IT systems or cloud servers. When everything is connected, issues related to managing a large number of connectivity devices and transmitting data securely also need to be addressed.
Industrial Networking Needs—Now and in the Future
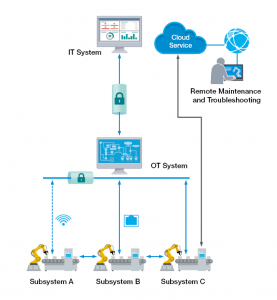
Besides enabling connectivity for previously unconnected OT assets, connecting all of these field devices also requires building a network that can support information flows among multiple interconnected devices, systems, and even remote sites. Consequently, you may want to consider incorporating the following elements into your industrial network infrastructure.
 Ethernet Network Nodes: A wide variety of managed or unmanaged Ethernet switches are available for building the Ethernet foundation of your LAN, integrating remote edge systems, and connecting the overall network.
Ethernet Network Nodes: A wide variety of managed or unmanaged Ethernet switches are available for building the Ethernet foundation of your LAN, integrating remote edge systems, and connecting the overall network.
Wireless Network Nodes: For hard-to-wire applications or those that require greater mobility, wireless LAN technologies can provide more cost-effective and flexible options instead of, or in addition to, wired Ethernet networks.
 Network Gatekeepers: Connecting field devices and OT assets to the Internet exposes your network to new cybersecurity risks. Secure routers and firewalls provide an excellent first line of defense that you will also want to consider.
Network Gatekeepers: Connecting field devices and OT assets to the Internet exposes your network to new cybersecurity risks. Secure routers and firewalls provide an excellent first line of defense that you will also want to consider.
Future-ready Industrial Networks: Many IIoT applications not only bring new business opportunities but also require more from our existing network infrastructure. To win the long-term networking game, it is essential to ensure your industrial networks can take on future challenges and opportunities.