A research team of Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences have discovered a soft robot, which can change its color and locomotion capabilities. The research team is led by professor Xuemin Du. Inspired by the color-changing capability of the chameleon, which can actively tune a lattice of light-reflecting nanocrystals in its top layer of skin to adapt to a changing environment, the structural color soft robot is able to sense modifications in the environment and exhibit vivid color alterations and programmable locomotion.
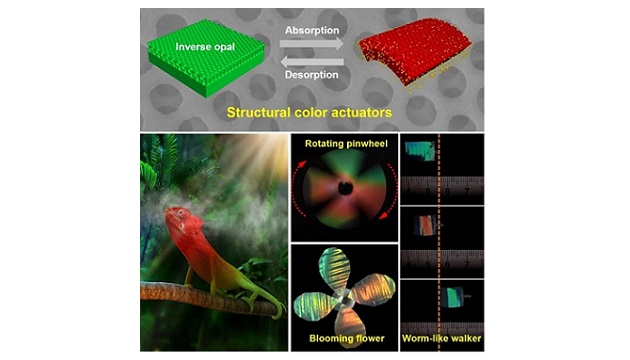
The robot’s instant and reversible color change results from the absorption or desorption of vapors into or from inverse opal films, which the researchers fabricated by using highly ordered silica colloidal crystals as structural templates. The exhibited colors can be tuned by varying the assembled particle size of the inverse opals or by changing the concentration of the driving vapors.
Various controllable shape transformations, including tube-curling, twisting, and rolling shapes, can be integrated to form an adaptive actuation system with synchronous changes in its shape and colors. Compared with other soft color actuators, the structural color actuator exhibits extremely rapid response (less than 1 s for color alteration and shape deformation) and robust actuation stabilities (greater than 110 cycles without obvious fatigue), the researchers said.
Various structural color actuators were constructed including a rotating pinwheel and a closing/blooming artificial flower. The researchers also designed a structural color walker by integrating an asymmetric design of frictions at the foreleg and hind leg into a patterned inverse opal film.
The researchers believe that various smart actuation systems with well-coordinated color and shape alteration could be developed by integrating intelligent functions, such as self-healing or self-adaptive capabilities, into the materials. By modifying the actuators to become aware of other stimuli, such as pressure, thermal, light, electric fields, and magnetic fields, many different types of robots that sense, respond, and interact with the environment could be created.