Wireless technology has already made a huge impact on our lives and it will only continue to do so to a point where we cannot imagine a time without it. Wireless capabilities offer convenience, portability and true functionality from anywhere. However, this functionality must work across platforms and across brands if the technology is to be widely adopted by end-users. Would-be competitors are therefore coming together to establish standards which ensure compatibility and/or interoperability to end-users. Whether we realize it or not, wireless technology has been all around us for quite some time. Radio, infrared, micro and sound waves penetrate our world in many forms – all without cables or wires. Wireless technology has gone one step further by providing data connections between computing devices and networks, and data connections between computing devices.
Wireless Overview
Today’s business environment consists of an increasingly mobile workforce. No longer chained to a desk for eight or more hours each day, employees equipped with notebook computers spend more time in situations outside of traditional work boundaries. They’re on the road, sitting in traffic, in between flights, in a taxi, working from a hotel room, or by the pool. Reliance on the Internet as a powerful information and communications medium has created a huge demand for 24/7 access, no matter what the location. Since most productivity occurs in meetings and away from desks, people require flexible access to a network in any conceivable situation.
Until now, that hasn’t been easy. But, once people experience and become accustomed to a particular computer or communications service in the office or home, they soon expect and demand similar capabilities while on the move. Remember how quickly desktop computers migrated to notebook computers? Consumers are demanding a similar transition for mobile multimedia capabilities for sound, data, images and video.
New innovative technologies allow access to the Internet, a corporate intranet or your own home-based network from wherever you can obtain cellphone service. And in an electronic future with smaller, cheaper, and more powerful devices, the speed and convenience at which information is accessible will be exponentially more important.
What does the wireless future hold? According to analysts, The future of wireless technology embraces soaring connectivity. New connected devices and applications not only escalate wireless bandwidth demand, they drive market growth for innovative network products, services and standards. The new wireless economy will probably enable us to have all our medical and financial records available at the click of a button. We are able to check and book travel itineraries in real-time while on the road. Cellular systems that remain constantly connected to the Internet, mobile videophones and mobile video conferencing. Wireless is revolutionizing telecommunications; new devices and personal connectivity together will drive the wireless future – no cables allowed.
The three main wireless categories covered are:
Wide area networks (WANs) – Using cellular phone systems to transmit data instead of voice Local area or wireless local area networks (LANs) – Used to connect several computers together in an office environment Personal area networks (PANs) – Used to create a connection between two or more portable devices without the need for cables or connectors. A brief overview on three main wireless categories: their benefits and limitations, standards, competing technologies, future trends and more.
Available Wireless Technologies
What are the differences between the wireless technologies available today?
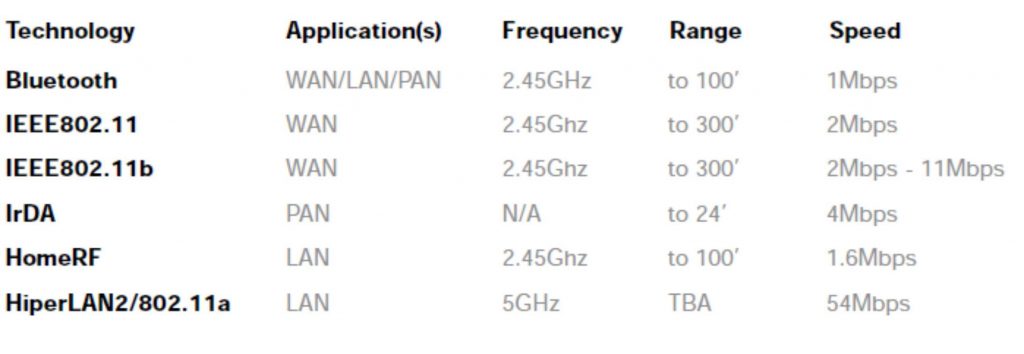
Bluetooth, IEEE 802.11b, HomeRF and HiperLAN all use radio frequencies to replace cables. But Bluetooth uses between 100 and 1000 times less power than established systems like 802.11b, while HomeRF is more expensive than Bluetooth to implement. And HiperLAN, although boasting greater data transmission speed, or bandwidth, currently requires more power than IEEE 802.11b and works over a shorter range.
Bluetooth
 Imagine a world where cables are not necessary, where many devices can communicate wirelessly, regardless of manufacturer or model. Imagine the ability to effortlessly connect to the Internet anytime, anywhere with only a mobile phone and notebook computer.
Imagine a world where cables are not necessary, where many devices can communicate wirelessly, regardless of manufacturer or model. Imagine the ability to effortlessly connect to the Internet anytime, anywhere with only a mobile phone and notebook computer.
This wireless connection between mobile phones and mobile computers has been the driving force behind the development of a new communications standard – Bluetooth.
Bluetooth is a new technology that eliminates the need for cables between electronic devices: PCs, mobile phones, headsets, handheld computers, printers, local area networks, etc. The technology is based on short-range radio transmission on a globally available frequency. Bluetooth provides convenient/quick, reliable, and secure wireless communications aimed at eliminating cables, connectors and adapters. It is a small design that is inexpensive to manufacture and install to ensure manufacturers will include it in all portable devices. Only a few millimetres in size, the Bluetooth module will revolutionise the world of wireless voice and data communications.
Bluetooth uses short-range radio, which offers an advantage over infrared solutions: walls, furniture, pockets or other obstructions no longer impede or compromise data transmissions. Connections are instant and maintained even when devices are not within line of sight. The range is approximately 10 meters, which you can extend to 100 meters. And because it’s designed for short-range radio transmissions, it will interfere as little as possible with other types of wireless devices in the vicinity. “Bluetooth uses between 100 and 1000 times less power and provides fast, reliable, and secure wireless communications.”
What are Toshiba’s global wireless initiatives?
Toshiba’s global wireless initiatives involve the development of a wide range of new products, the enhancement of existing products, and the formation of alliances with key strategic partners from the hardware, software, networking and telecommunications sectors. Designed to meet a wide range of customer needs, Toshiba’s wireless products and services will be developed in three different segments: Wide Area Networks (WAN); Local Area Networks (LAN); and “personal area’’ connectivity, that is, cable replacement and Personal Area Networks (PAN).
Within Japan, many different laboratories (researching communication platforms, multimedia devices, mobile communications, computer and network systems) and development centres (for mobile computing and communications, personal and multimedia systems, computer and network systems) are working on applied research in the area of wireless technology.









