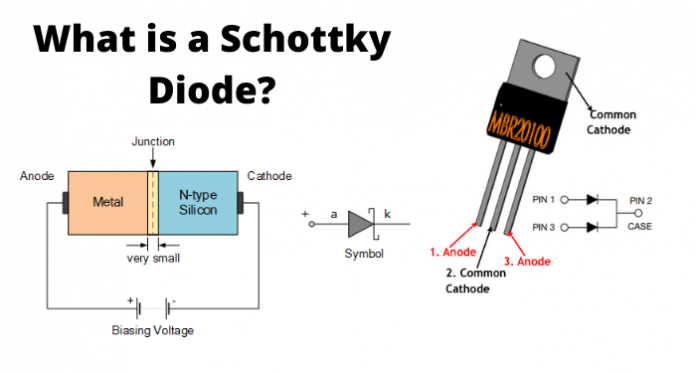
Schottky diode, also known as the hot-carrier diode is a semiconductor diode with a very fast switching action, but a low forward voltage drop. When a current flows through the diode there is a small voltage drop across the diode terminals. In a normal diode, the voltage drop is between 0.6 to 1.7 volts, while in a Schottky diode the voltage drop normally ranges between 0.15 and 0.45volts. This lower voltage drop provides a higher switching speed and better system efficiency. In Schottkys diode, a semiconductor–metal junction is formed between a semiconductor and a metal, thus creating a Schottky barrier. The N-type semiconductor acts as a cathode and the metal side acts as the anode of the diode.
E.g.: Solar panel, power supplies.