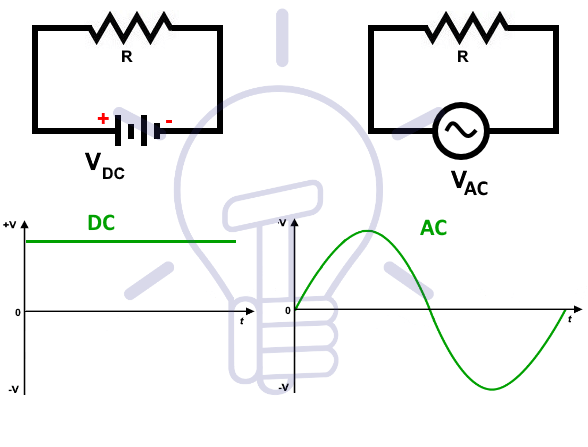
AC stands for Standard Current is the flow of charge that changes direction periodically. As a result, the voltage level also reverses along with the current. AC is used to deliver power to houses, office buildings, etc. AC can be produced using a device called an alternator. This device is a special type of electrical generator designed to produce alternating current. Alternating Current can come in a number of forms, as long as the voltage and current are alternating. Home and office outlets are almost always Alternating Current. This is because generating and transporting Alternating Current across long distances is relatively easy. Alternating Current is also capable of powering electric motors. Motors and generators are the exact same device, but motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. This is useful for many large appliances like dishwashers, refrigerators, and so on, which run on Alternating Current.
DC stands for Direct Current is the electric current only flows in one direction, rather than oscillating back and forth, DC provides a constant voltage or current. DC can be generated in a number of ways:
- An AC generator equipped with a device called a commutator can produce direct current
- Use of a device called a rectifier that converts AC to DC
- Batteries provide DC, which is generated from a chemical reaction inside of the battery
Everything that runs off of a battery, plugs into the wall with an AC adapter, or uses a USB cable for power relies on DC. Examples of DC electronics include:
- Cell phones
- The LilyPad-based D&D Dice Gauntlet
- Flat-screen TVs (AC goes into the TV, which is converted to DC)
- Flashlights
- Hybrid and electric vehicles