It has been said many times, but 5G is more than just more speed and lower latency, it is a whole new way of architecture for mobile networks with a number of interesting new capabilities which lead to interesting new applications.
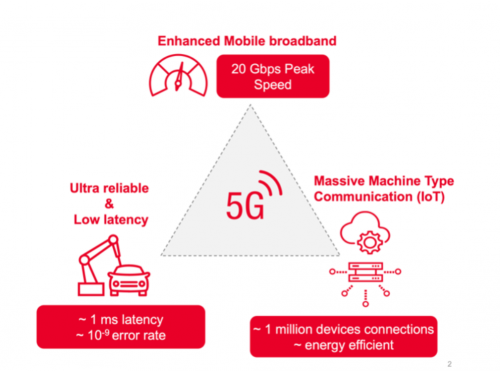
The primary capabilities, enhanced mobile broadband, ultra reliable low latency communications and massive machine type communications are detailed below:
- eMBB – enhanced mobile broadband – download speeds reaching 20 Gbps – enabling high speed mobile hotspots, enhanced multimedia (VR/AR, 4K+ streaming, etc.)
- uRRLC – ultra reliable low latency communications – very fast (1ms) and very reliable (10^-9 error rate) – enabling remote surgery/telemedicine, cloud robotics manufacturing
- mMTC – massive machine type communications – enabling very high device densities (1m+ devices per sq KM) while preserving energy efficiency and managing congestion in IoT applications
These capabilities and use cases bring with them certain assumptions and certain requirements of the transport network which will impact approaches used to validate that network. One example of this is the need to have TSN (time sensitive networking) in the fronthaul network between the radio unit (RU) and the distributed unit (DU), particularly when supporting uRRLC.
TSN and Ethernet are strange bedfellows because Ethernet was originally built with the intent that delivery was to be best effort and that data would get there when it got there. When dealing with 5G this is no longer good enough, which is where frame preemption comes in. When the network sees traffic is going to create contention, pre-emptible frames can be paused to allow express frames through in order to enable appropriate. When you factor in fragmentation, reassembly and other factors is it more complex than it might seem at first.
Some areas to test include latency of express traffic in the presence of preemption and validation of reassembly of preempted traffic. What we are trying to do here is determine if your device under test allow the express traffic to pass through with appropriate timing and whether or not this impacts other traffic on that device.
This is where our IxNetwork software for L23 testing running on the Ixia Novus SFP28/QSFP28 High Density 100/25/10GE Load Module comes in. With support for TSN frame preemption (802.1Qbu / 802.13br), time aware shaping (802.1Qbv) and a variety of 1588v2 profiles, this Ixia Novus load module is ideal for validating 5G RAN transport. To make things even easier for the QA engineer charged with testing frame preemption, using experience gained building industrial and automotive test solutions, we have included a TSN wizard in IxNetwork, reducing time and guesswork in test setup.