By: Jami McGraw, Technology Director, Arrow
The landscape of data processing is undergoing a massive shift. As artificial intelligence (AI) and particularly Generative (Gen) AI continue the relentless march forward, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) face a critical question: where will the data be processed and stored? Let’s delve into the evolving world of far edge, near edge, and on-premise computing, exploring the considerations for OEMs seeking to build Gen AI solutions.
Gen AI, while powerful at the edge, introduces some unique challenges to edge infrastructure, including:
- Massive datasets: Gen AI algorithms often require vast amounts of training data, which can strain far edge and near edge resources.
- Limited processing power: Gen AI models are computationally intensive. Edge devices, often with limited processing power compared to on-premise servers, can struggle to run complex Gen AI models efficiently.
- Real-time or near real-time needs: Certain Gen AI applications, like personalized recommendations or anomaly detection, might necessitate real-time or near real-time processing, pushing the boundaries of latency tolerance.
The traditional centralized data processing model in the cloud is giving way to a more distributed approach. Leveraging a combination of far edge, near edge, and cloud resources can distribute the processing load. Far edge devices can perform initial data collection and pre-processing, while near edge nodes handle preliminary training and filtering. Complex Gen AI computations can then be offloaded to on-premise data centers or the cloud.
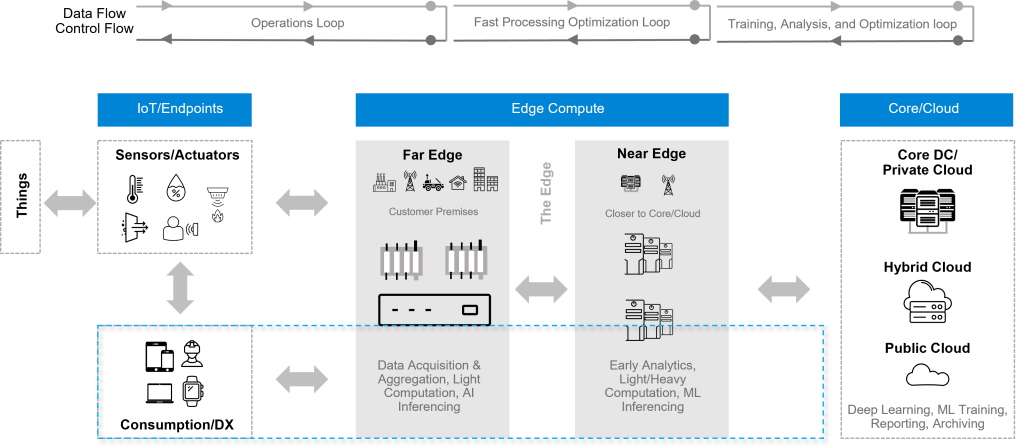
Far Edge Computing: Extending the Boundaries
Far edge computing refers to processing data at the outermost edge of the network, close to where data is generated, which is particularly beneficial in scenarios where low latency and real-time processing are crucial.
| Applications in Gen AI | Advantages of Far-Edge Processing |
| Smart Surveillance and Security: Gen AI models at the far edge can analyze video feeds in real time to detect threats and recognize faces, reducing the need for data transmission to central servers.
Autonomous Robots or VehiclesB Robots and vehicles equipped with edge devices can instantaneously process sensor and camera data, enabling safer navigation and obstacle avoidance. |
Reduced Latency: 5 to 20 ms. Immediate data processing near the source.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Less data goes to centralized cloud systems. Enhanced Privacy: Local data processing mitigates the risk of data breaches. |
Near Edge Computing: Bridging the Gap
Acting as a bridge between far edge devices and the cloud, near edge devices offer more processing power than their far edge counterparts. Gateways, local servers, and fog computing nodes typically reside at the near edge, handling tasks like data aggregation, filtering, and preliminary analytics.
| Applications in Gen AI | Advantages of Near-Edge Processing |
| Retail: Near edge devices can analyze customer behavior in real time to provide personalized shopping experiences and manage inventory efficiently.
Smart Cities: Environmental monitoring systems at the near edge can swiftly process and respond to data on air quality, noise levels, and traffic patterns. |
Balanced Latency: Up to 50 ms. Quicker than centralized processing, suitable for applications that require timely responses but are not instantaneous.
Scalability: Easier to scale across multiple locations compared to far edge devices. Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for extensive infrastructure at the far edge. |
On-Premise/Cloud Computing: Control and Customization
On-premise computing involves deploying and managing computing resources within the organization’s physical location. This approach offers high levels of control and security but can be less scalable than cloud-based solutions.
| Applications in Gen AI | Advantage of On-Premise/Cloud Processing |
| Healthcare: Hospitals can use on-premise Gen AI systems to analyze medical imaging and patient data, ensuring compliance with stringent data privacy regulations.
Industrial IoT (IIoT): Manufacturing plants can deploy AI models to monitor machinery and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime and improving productivity. |
Complete Control: Full data and infrastructure ownership allows for tailored solutions.
Enhanced Security: Data remains within the organization’s premises, reducing exposure to external threats. Customization: Flexibility to customize hardware and software to specific requirements. |
6 Considerations for OEMs: Selecting the Right Infrastructure
The choice between far edge, near edge, and on-premise processing depends on several factors for OEMs:
- Data volume and complexity: For applications generating large volumes of complex data, near edge or on-premise solutions might be necessary. Conversely, low-volume sensor data might be well-suited for far edge processing.
- Latency requirements: Real-time decision-making often necessitates on-site processing. Applications requiring minimal delay might favor near edge or on-premise solutions over the cloud.
- Security and privacy: Far or near edge processing can offer greater control and security for sensitive data. Regulatory compliance might also dictate processing location.
- Cost and scalability: Cloud-based solutions provide scalability and eliminate the need for upfront hardware investment. However, on-premise solutions can provide greater cost control over time.
- Power availability: Far edge devices often operate on limited power, necessitating efficient processing with minimal resource consumption.
- Operating environments: Temperature variations, dust, noise, and humidity are factors when determining where to deploy the infrastructure.
Summary: The Future is Distributed
The future of data processing lies in a distributed approach, with far edge, near edge, and on-premise solutions working in concert with the cloud. As Gen AI evolves, OEMs must adopt flexible and scalable processing strategies. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each processing platform and implementing a hybrid approach when necessary, OEMs can ensure their solutions effectively leverage the power of AI at the edge.
Companies looking to leverage Gen AI at the edge can benefit from the combined expertise of Arrow and Dell OEM Solutions. Dell’s robust portfolio provides the ideal building blocks for far edge, near edge, and on-premise deployments. Arrow can guide companies through the process, from selecting the optimal hardware for their Gen AI application to helping ensure a smooth supply chain and offering implementation support. Their expertise in solution orchestration enables companies to deploy and manage their Gen AI solutions at the edge with greater efficiency and reduced risk.









