Navigating the world of modern design is complex. It’s filled with new challenges and fast-paced changes in technology. You need a robust requirements management process to manage these challenges successfully to ensure your design intent communication stays clear and organized. Read on to explore the crucial connection between well-managed requirements and today’s design.
What Are Requirements?
Requirements are the must-have features and functions your product needs to be successful. They guide you step by step, ensuring that what you build will meet the expectations and needs of the people who will use it.
Think of requirements as answers to specific questions:
- What does it need to do?This could be anything from making calls and sending messages on the phone to the speed and mileage of a car.
- Why is this important?This helps understand the value of each feature, ensuring that it has a clear purpose and benefit.
- How will I know it works as it should?This part helps in testing and verifying that each feature functions correctly.
Requirements come from different places and people, like customers, partners, sales, support, management, engineering—anyone with a stake in the project. Everyone brings their own needs and expectations, and it’s crucial to listen, understand, and include these in the planning and design process. Requirements are the building blocks that help ensure the final product does exactly what it’s supposed to do, satisfying users’ needs and expectations, and ultimately becoming a success.
Types of Requirements
You can discern many different types of requirements depending on a specific need they must fulfill, for example:
- Functional requirementsare the fundamental aspects that a product or system must possess to meet its intended purpose. They define what the product must do, outlining the necessary functions and features to meet user needs and expectations. For a washing machine, these could be that it should wash various fabrics, rinse, and spin the clothes to remove excess water.
- Performance requirementsdictate how well a product or system performs its functions. They encompass aspects such as efficiency, responsiveness, and speed, ensuring that the product operates optimally under defined conditions. Performance requirements for a washing machine might specify that it shouldn’t consume more than 400 kWh of electricity and 40 gallons of water per cycle.
- Constraint requirementsare the restrictions within which a product must operate. These could relate to size, cost, or technical capabilities, setting boundaries that guide the design and development process. For the washing machine in question, they could involve weighing less than 150 pounds and being at most 27 inches wide, 39 inches tall, and 34 inches deep.
- Environmental requirementsfocus on a product’s interaction with its environment, ensuring it operates effectively under various conditions and adheres to sustainability and ecological standards. Environmental specifications for our washing machine could dictate energy efficiency and water-saving qualities.
- Interface requirementsare centered around user experience, making sure the product is user-friendly, accessible, and easy to use. They promote a positive interaction between the user and the product or system. In our case, it could mean that the washing machine’s control panel should be user-friendly and intuitive, having buttons and dials clearly labeled with easily understandable icons and text to indicate their function.
What Is Requirements Management?
Requirements management is a set of techniques for recording, examining, ranking, and consolidating requirements, ensuring that engineering teams consistently work with up-to-date and approved specifications. Its aim is to guarantee the achievement of product development objectives. By meticulously monitoring alterations in requirements and promoting ongoing communication with stakeholders, requirements management minimizes errors, maintaining alignment and clarity from the project’s start through the entirety of the engineering lifecycle.
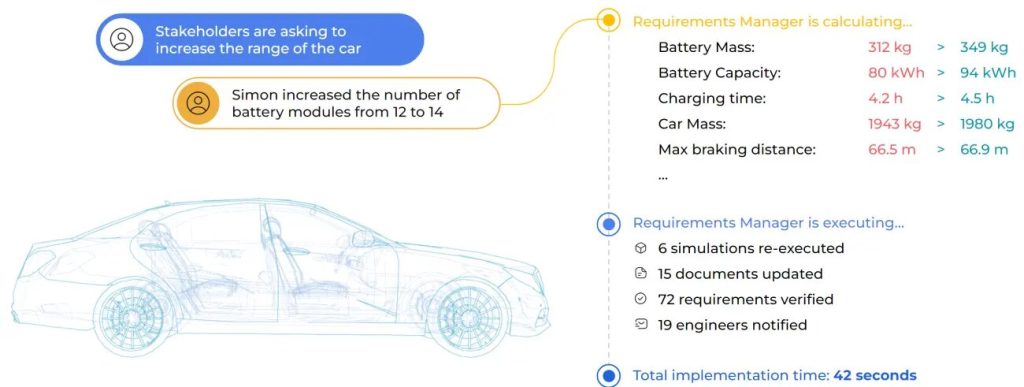
An essential aspect of requirements management is its ability to de-risk projects from unexpected and late-stage requirement changes. For instance, consider the complex process of car design. If a stakeholder requests an increase in the vehicle’s range, it would necessitate various adjustments, such as increasing the number of battery modules. A tool for managing compliance statuses, like the Altium 365 Requirements Manager, automatically recalculates all relevant properties, like battery mass and capacity, and adjacent properties, such as charging mass, car mass, and braking distance, ensuring full traceability of the change and its system-wide impact.
In a traditional setting, accommodating a new requirement would involve a tedious chain of meetings, emails, and manual updates, often extending over weeks. With a proficient requirements management tool, you can drastically reduce this time because every team member is aligned, informed, and working on the latest, most accurate information within seconds. All aspects of the design are consistently synchronized, and no detail is overlooked or forgotten in the fast-paced development lifecycle. You can finish your car design updates within a minute instead of weeks of disjointed, back-and-forth communication.
The Challenges of Modern Design
While the concept of requirements is easy to grasp, the speed and complexity of modern design development complicate the overall picture. We’re witnessing an unprecedented pace of technological advancement and a surge in the intricacy of electronic designs. This evolution, while exciting, brings forth a multitude of challenges that necessitate a structured approach to requirements management.
#1 Complexity of Electronic Designs
The proliferation of smart devices has exponentially increased the complexity of electronic designs. For instance, chip usage in products has skyrocketed, with modern vehicles incorporating over 2,000 chips, a staggering increase compared to a few decades ago. Such complexity necessitates precise and well-organized requirements to navigate the intricate web of design elements, ensuring that each component integrates smoothly to function as a cohesive whole.
The more complex the product, the more critical becomes the significance of requirements management. This is because more time and budget are invested in its development. The cost of getting it wrong—be it money, time, or reputation—is too great to risk.
#2 Growing Software Interconnection
Software has become an integral part of products, with the lines of code embedded in them soaring fifteenfold over the last decade. Software acts as the communication bridge, enabling various hardware systems to exchange critical information. This intricate web of interconnectivity demands well-established communication protocols to secure the uninterrupted flow of essential data. An unexpected alteration in the requirements of one system can disrupt this harmonious interaction, leading to unforeseen complications and extensive rework. Thus, the role of requirements management becomes crucial in safeguarding the stability and reliability of these interconnected systems to maintain the integrity of the overall communication network.
#3 Reduced Production Timelines
The urgency to expedite product delivery has led to a significant reduction in production timelines. Traditional five-year cycles have been compressed to two, calling for agile methodologies that emphasize swift iterations and continuous improvement. In such a fast-paced environment, having clear and well-defined requirements is crucial to guide the design process efficiently and facilitate quick decision-making.
#4 Communication Gaps and Siloed Processes
Design processes have been plagued by communication gaps, with electronic data often existing in isolated silos. The exchange of information between these silos is a manual and inefficient process, leading to the unnecessary expenditure of valuable time and resources and compromising the overall quality of the product. A robust requirements management system acts as a unifying thread, enhancing communication and ensuring all design aspects are aligned and integrated.
#5 Lack of Traceability
It’s quite common for as many as 80% of designs to experience last-minute changes in components due to constraints related to cost or availability. The absence of traceability in such modifications can lead to confusion and errors, often derailing the entire design process. Requirements management fosters traceability and ensures that each modification is documented and aligned with the overall design objectives, thus minimizing mistakes and enhancing the design’s integrity.
7 Reasons Requirements Management Is Essential
As you see from the above analysis, requirements management is not optional. It’s essential to secure the project’s success, especially in light of the fact that poor requirements trigger 70% of project failures. Inaccurately defined requirements can lead to expanding project scopes, delayed timelines, escalated costs, and a final product that falls short of meeting customer expectations and safety standards. Adopting a structured attitude toward their management can prevent your project from becoming another failure in the quoted statistics.
#1 Clarifying Objectives and Expectations
Requirement management clarifies the project’s objectives, aligning stakeholders like product managers, designers, developers, and clients towards a unified goal. It provides a clear roadmap, outlining the project’s scope, budget, and schedule, ensuring that every step is well-planned and executed according to the established objectives and expectations.
#2 Faster Delivery
Managing compliance status promotes timeliness, helping projects stay on schedule for quicker delivery while upholding quality standards.
#3 Reusability
Requirements management allows for the reuse of specific project components in subsequent projects, enhancing sustainability and efficiency throughout development.
#4 Improving Quality and Reducing Errors
A clear set of requirements minimizes errors, misunderstandings, and omissions in the design process, ensuring that the final product meets expected quality standards and fulfills its intended purpose. Requirements management enhances the alignment of the end product with customer needs and expectations, thereby improving its overall quality.
#5 Lower Cost of Development Across the Lifecycle
Lifecycle Insights reports that companies, on average, encounter 2.8 board respins, each costing approximately $46,000. Errors in requirements often necessitate extensive rework by the development team. The cost of correcting a software error escalates if the mistake is detected later in the process. The necessity to reduce these costs is beyond question, and strategies that minimize requirement discrepancies are most welcome.
Effective requirements management enhances project efficiency and accuracy. It minimizes unnecessary expenses throughout the project, leading to a more economical development process. It also aids in reducing the frequency of costly and time-consuming modifications, saving both money and months of extra work.
#6 Risk Management
Requirements management helps identify potential risks early in the project, allowing for implementing strategies to mitigate them.
#7 Facilitating Communication and Collaboration
Working with a transparent and well-managed set of requirements fosters effective communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders. It acts as a common language, improving understanding and cooperation across various domains of expertise.
Design Faster with Fewer Errors
The complexities and rapid advancements in modern design call for a strong foundation in requirements management. A well-organized set of specifications supports the process by providing clarity, enhancing communication, and ensuring that the design evolves cohesively in the desired direction. Check it on your own using Requirements Manager. Design faster with fewer errors!