Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 835 sports a 35% decrease in package size with 25% better power efficiency compared to the existing 821.
With a 35% decrease in package size and 25% better power efficiency compared to existing 821, the 10nm Snapdragon 835, which was recently released at CES 2017 by Qualcomm, upgrades across all its subsystems that analysts called impressive but evolutionary.
Interestingly, the 835 is also the company’s first ARM-based processor to support Windows 10 on a mobile device.
“This is big news with Microsoft adding x86 emulation on ARM to Windows 10,” said Kevin Krewell, principal analyst at Tirias Research. “I see this as a real threat to Intel. It may also be a step in Microsoft bringing Windows server to ARM as well,” he added.
The 835 is expected to debut in the next generation of premium smartphones when it ships in the first half of 2017. Its predecessors, the 820/821, were used in smartphones including the Google Pixel, the LG G5 and the Galaxy S7/Edge.
“We see the forthcoming 2017 mobile processors as mostly offering evolutionary improvements, but nothing significantly new,” said Mike Demler, senior analyst at the Linley Group.
“Qualcomm’s LTE-Advanced modems offer higher connection speeds at every generation, but those speeds are rarely experienced in real world conditions,” Demler said.
“I’m expecting the 835 to be the highest performing Android smartphone SoC and the highest performance graphics, VR and AR of any smartphone, including Apple,” said Patrick Moorhead, president of Moor Insight & Strategy.
The Snapdragon 835 may not deliver anything groundbreaking, but it does maintain the company’s leadership in mobile SoCs.
“Samsung is likely to continue using a mix of its own Exynos and Qualcomm Snapdragon processors,” said Demler.
“Apple tends to emphasise graphics performance, hence their customised PowerVR GPU. The latest Apple A10 CPU scores highest in our comparisons, so that will likely get even better at 10nm” he added.
Improvements on Qualcomm’s SoC
Qualcomm said the 835 is designed to support “next-generation entertainment and connected cloud services” in a range of consumer devices, including smartphones, VR/AR head-mounted displays, IP cameras, tablets, mobile PCs and other devices running Android and Windows 10.
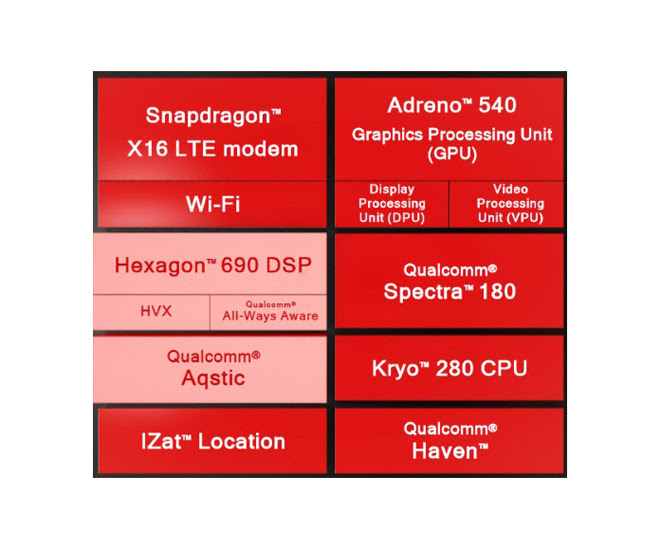
The SoC sports the Kyro 280 CPU with four performance cores running at up to 2.45GHz and four efficiency cores running up to 1.9GHz. Compared to the 821’s Kyro 260, that’s a slight performance bump of 0.05GHz in clock speed, but a notable upgrade in power efficiency: Kyro 280 doubles the number of efficiency cores of the 260.
The Symphony System Manager tool returns in the 835, enabling OEM and Android developers to specify which core should run each task. The 835 upgrades the Hexagon 682 DSP to support Google’s TensorFlow machine learning framework and Halide, a programming language for digital imaging.
Qualcomm foresees VR as just the first step in what may be a 30-year road map culminating in augmented reality systems that subsume virtual reality headsets. The 835 takes one step in that direction with upgrades to the Adreno visual processing subsystem.
The Adreno 540 has a 25% increase in 3D graphics rendering performance, support for up to 60x more colors and a 10-bit color gamut. Qualcomm claims the 835 is the first mobile SoC to deliver 4K capture (H.264) and playback needed for Ultra HD Premium.
A new feature called Q-Sync matches the display’s refresh rate with the GPU’s render rate to eliminate sudden frame rate drops. However, it’s unclear whether the Adreno 540 can deliver VR at 120fps.
The Spectra 180 imaging processor features two 14-bit pipelines that permit the use of a single 32MP or dual 16MP cameras. Additional features like smooth optical zoom, fast auto-focus and hybrid autofocus enhances photography, while “perceptual quantisation” improves video quality by using machine learning to adjust encoding bit rates based on scene relevance.
For all the bells and whistles, network bandwidth remains the real gatekeeper of next generation mobile computing. So the X16 LTE modem in the 835 supports several LTE technologies that pave the way to 5G, including 3x carrier aggregation, 4×4 MIMO and 256 QAM. Together, they achieve an LTE Category 16 throughput of up to 979Mbits/s—a nearly 50% improvement over the X12 LTE in the Snapdragon 821 with its Cat 12 support.
The 16X LTE modem has Bluetooth 5 and integrated 2×2 Wi-Fi supporting 802.11ac MU-MIMO with up to 50% reduction in size and a 60% reduction in Wi-Fi power consumption compared to the 820.









