In our digital world, software is the engine that drives us forward. Companies can only grow if their software infrastructure allows. But what happens when your in-house tools cannot keep up with emerging technologies, software innovation, or your future business goals?
Keysight commissioned Forrester Consulting to survey software testing decision-makers at global enterprises to research their current software testing approach and how their approach will impact their future business decisions.
Weighing the pros and cons of in-house testing vs. automated software testing solutions
Software testing is an essential part of the software development lifecycle. It ensures that applications are high quality, meet end-user requirements, and are free from defects or bugs. Many organizations use their resources and expertise to perform software testing in-house. However, as Forrester found, decision-makers have several compelling reasons to move to a commercial software testing solution from an in-house one.
Commercial software testing
Commercial software testing solutions are designed to help organizations improve the quality of their software and reduce time-to-market. By leveraging the latest testing tools, methodologies, and best practices, these solutions can help organizations identify defects and bugs earlier in the software development lifecycle. Additionally, commercial solutions can lead to reduced development costs and improved software quality. Organizations can free up their resources and focus on core business activities, which can help accelerate time-to-market.
According to Forrester’s research data, respondents stated that using commercial solutions to reduce testing costs was the biggest business improvement their organizations expected. Furthermore, the impact was significant or transformational for their organizations.
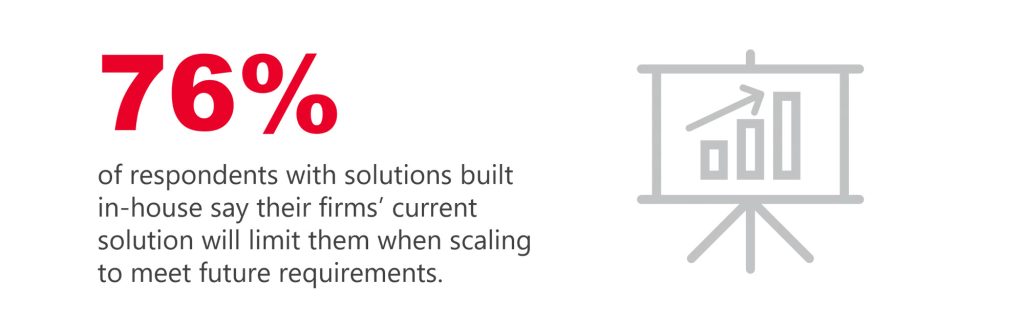
In-house software testing
One key finding of the study was that in-house solutions could weigh heavily on a company’s productivity and resources. According to the research, respondents with in-house solutions expect their automation investments will have a less significant impact on their organization’s ability to scale and reduce overall testing costs than those with commercially built solutions.
Also, of the respondents with in-house solutions, sixty-three percent use three or more development tools or automation solutions to conduct their testing. Having multiple dispersed testing tools costs much more than a single test automation platform.
In addition, despite having more tools at their disposal, a vast majority disclose that they are doing a lot of time-consuming and expensive manual testing to bridge gaps.
While solutions built in-house may initially appear to be more cost-effective, they underdeliver on these promises as buyers realize the reality of hidden costs associated with their implementation and maintenance.
In contrast, according to the research, respondents using commercial software testing solutions only require one or two to meet their testing needs, requiring less manual intervention.
Inability to scale and increased software testing complexities drive change
In today’s competitive business landscape, business leaders seek opportunities to scale. Keeping up with the latest technologies is crucial to staying competitive. The Forrester study states, “Companies must mature their automation strategy to meet customer demands and deliver at scale.”
While in-house software testing can be cost-effective in some cases, it can also be expensive, especially when considering the costs of hiring and training specialized staff, purchasing and maintaining testing infrastructure and tools, and managing testing projects.
According to the report, the inability to scale is a tipping point for organizations with in-house solutions. As companies strive to streamline their technology, they often encounter the challenge of integrating legacy applications and mainframe systems against a more modernized technology stack.
Because of the vastly different infrastructure, these systems require extensive testing to ensure the user experience is not compromised. Unfortunately, relying on open-source and manual testing for these complex systems is not robust enough.
Barriers to transforming to an automated software test approach
Time spent writing scripts, fixing bugs, and manually testing all possible user journeys can quickly add up and often becomes the bottleneck when implementing a new feature release. Consequently, automation growth stalls and companies cannot deliver differentiable, high-quality products.
Forrester asked what barriers prevented companies from investing or continuing to invest in automated testing technologies.
- Forty-six percent of participants stated they lacked the in-house expertise to implement and/or maintain a platform.
- Forty-six percent said they lacked funding.
- Thirty-six percent said they lacked the skills necessary to define the requirements.
Technological advancements increase software testing challenges
Technology complexity is a growing challenge and requires higher-level tools. Even scripted automation is not enough. The new generation of software testing needs to provide advanced analytics algorithms tuned to the evolving challenges and the use of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to solve complex problems.
As companies strive to streamline their technology, they often encounter the challenge of integrating legacy applications and mainframe systems against a more modernized technology stack. Because of the vastly different infrastructure, these systems require extensive testing to ensure the user experience is not compromised.
The dramatic shift to online services witnessed over the last decade has forced enterprises to become more adaptive. As companies continue their digital journeys and technological innovations accelerate, transitioning to software testing automation is becoming a necessity.
To be successful, organizations need a software testing solution that will allow them to scale adequately and affordably, align with current and future technologies, and ensure compliance with increasingly complex software testing requirements.