The global adoption of 5G wireless networks has been slower than anticipated, with high costs, limited coverage, and the lack of necessity for some advanced features contributing to this lag. However, the introduction of the Reduced Capability (RedCap) standard by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) in 2021 aims to accelerate 5G’s expansion into new markets, including industrial, medical, home and buildings, and security sectors.
What is 5G RedCap?
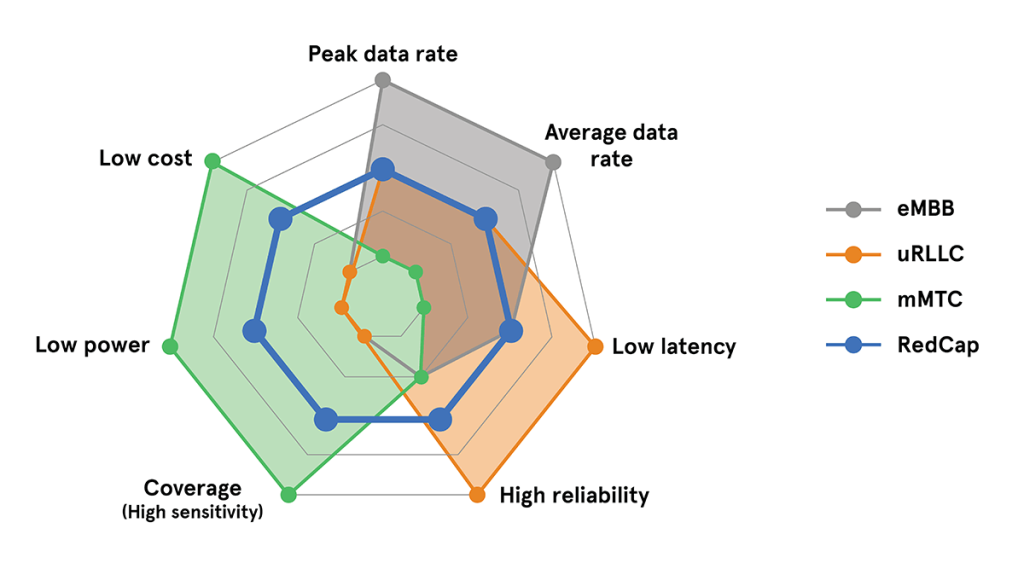
5G RedCap, also known as 5G NR-Light or New Radio-Lite, is a simplified version of the 5G standard that bridges the gap between 4G and 5G. It is designed for use cases with minimal hardware requirements, where ultra-high data rates, ultra-low latency, or extremely low power are not essential, but reliable throughput is still necessary. RedCap devices are less complex and more cost-effective compared to baseline 5G devices defined by the 5G Release 15 standard.
One of the key features of RedCap devices is their ability to operate with a single receiving antenna, which reduces complexity and integration costs. These devices also incorporate low-power features like radio resource management (RRM) relaxation and extended Discontinuous Reception Mode (eDRX). These enhancements are particularly advantageous for applications involving static objects or devices that primarily upload data to the cloud, as they can significantly benefit from the resulting power savings.
Looking ahead, Enhanced Reduced Capability (eRedCap) is set to build on the benefits of RedCap by offering even smaller throughput while utilizing the same 5G standalone (SA) network.
5G RedCap: The Next Step Beyond LTE for IoT Connectivity
5G RedCap and its enhanced version, eRedCap, represent the future of mid-end cellular IoT connectivity. These technologies are poised to replace LTE Cat 4 and LTE Cat 1 in the coming years, offering a more efficient solution for industrial, medical, and automotive markets that demand longevity. While it may be too early to discuss the phasing out of 4G, it is clear that from a cellular network and chipset perspective, further evolutions of 4G are unlikely.
RedCap increases the addressable 5G market by providing a functional middle ground between high-performance 5G and low-end cellular communication technologies like LTE-M and NB-IoT. Some use cases are already well-served by LTE, but new opportunities are emerging that are better suited to RedCap’s capabilities.
5G RedCap Set to Capture 18% of IoT Market by 2030
The market potential for 5G RedCap is significant, particularly in regions where cost is a critical factor for the widespread adoption of digital technologies. According to the Global Cellular IoT Module Forecast, 5G RedCap modules are projected to represent 18% of all cellular IoT module shipments by 2030. This projection highlights the growing importance of RedCap technology, especially in developing nations.
5G RedCap is specifically designed to address emerging use cases that are not adequately served by existing advanced 5G standards, such as NB-IoT, Cat-M1, and 4G. With chipsets already available, 5G RedCap is poised for growth, offering reduced data flow and dependable connectivity while optimizing power consumption to significantly extend device battery life.
The flexibility and network advantages of 5G RedCap, including lower latency, higher speeds, and improved power efficiency compared to previous LTE generations, position it as a superior choice for future mass IoT deployments.
5G RedCap Powers Wearables, Surveillance, Medical Devices, and Industrial IoT: Use Cases
5G RedCap is ideally suited for a diverse array of IoT applications, such as:
- Smart Wearables: Devices like smartwatches and low-end XR glasses can benefit from RedCap’s balance of performance and power efficiency.
- Video Surveillance: RedCap’s reliable connectivity and higher data rates are ideal for video surveillance applications.
- Medical Devices: Health monitors and other medical devices can leverage RedCap’s low latency and power efficiency.
- Utility/Smart Grid/Industrial Gateways: RedCap’s dependable connectivity makes it an excellent choice for utility and industrial applications.
Benefits for IoT Applications
5G RedCap provides several important advantages for IoT applications:
- Increased Peak Data Rate: RedCap can achieve peak data rates up to three times higher than LTE Cat 4, making it ideal for applications that demand greater data throughput.
- Higher Peak Data Rate: RedCap is capable of delivering peak data rates up to three times faster than LTE Cat 4, making it well-suited for applications that demand higher data throughput.
- Lower Latency: RedCap offers latency comparable to existing 4G LTE technologies, supporting near real-time data communication for applications like industrial automation and smart grids.
- Improved Power Consumption: By enhancing power efficiency, RedCap can extend the battery life of IoT devices, which is critical for long-term deployments.
Conclusion
5G RedCap represents a significant leap forward in 5G technology, specifically tailored to bridge the gap between high-speed enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), ultra-reliable low latency communications (uRLLC), and low-throughput, battery-efficient Massive Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) use cases.
With chipsets already available and the potential for significant market growth, 5G RedCap is set to play a pivotal role in future IoT deployments, offering a flexible, efficient, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications. As 5G continues to evolve, RedCap’s role in expanding device connectivity and driving innovation will only grow, making it an essential technology for semiconductor manufacturers, OEMs, and the broader IoT ecosystem.









