Scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have developed a tool to monitor communications within the brain in a way never before possible, and it has already offered an explanation for why Alzheimer’s drugs have limited effectiveness and why patients get much worse after going off of them.
The researchers expect their new method will have a tremendous impact on our understanding of depression, sleep disorders, autism, neurological diseases, and major psychiatric conditions. It will speed scientific research into the workings of the brain, they say, and facilitate the development of new treatments.
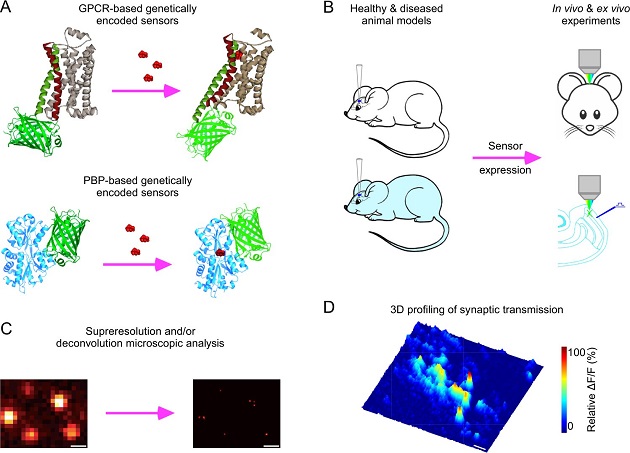
The new method developed examines transmissions inside the brain at both the microscopic level and the far, far smaller nanoscopic level. It combines a biological “sensor” with two different forms of cutting-edge imaging.
The approach can quantify “neuromodulatory” transmissions, which are associated with major brain disorders, including addiction, Alzheimer’s, depressive disorders, and schizophrenia. They’re also linked to autism, epilepsy, eating disorders, and sleep disorders
Neuromodulatory transmissions are the “slower” transmissions in the brain. They’re typically thought to involve lots of neurons in large regions. That’s in contrast to the much faster transmissions that happen neuron-to-neuron.
In Alzheimer’s disease, scientists discovered a surprising degree of “fine control and precision” in the supposedly shotgun neuromodulatory transmissions. Widely used Alzheimer’s drugs known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors may inhibit this precise communication, the scientists report. That may explain the limited effectiveness of the drugs, they say.
The researchers went on to identify potential changes in the brain that could be brought about by long-term use of the drugs, which could explain why patients often get much worse when they stop taking them. The new method points out Alzheimer’s defects in unprecedented spatial and temporal resolution, defining the precise targets for medicine.
Alzheimer’s, the researchers say, is just the tip of the iceberg. The new system has “broad applicability” across the spectrum of neurological and psychiatric diseases and disorders, they report in two new scientific papers. In the years to come, the scientists predict, it will help doctors understand neurological illnesses and psychiatric problems, screen drugs for potential treatments, identify disease-causing genes, and develop better, more personalized medicine tailored for specific patient needs.