Nanoscribe enables 3D Printing of Micro-Optics
The German company Nanoscribe is developing and producing high-precision 3D printing solutions enabling the micro-optics industry to innovate by additive manufacturing. Typically, the benefits of additive manufacturing are considered to be fast and flexible design iterations as well as freedom of design. But the usual 3D printing technologies available in the market fail to meet the resolution and precision requirements of optical applications.
However, a broad range of almost arbitrary micro-optical shapes including standard refractive micro-optics, freeform optics, diffractive optical elements or even multiplet lens systems can now be printed in a one-step-process by means of Nanoscribe’s Photonic Professional GT 3D printers, tailored solutions and materials.
The additive manufacturing approach allows to directly fabricate micro-optical components from polymers with optically smooth surfaces, high shape accuracy and significantly smaller geometrical and design constraints than standard fabrication methods.
The additive manufacturing workflow also drastically shortens the design-iteration phase and ideas can be turned into functional prototypes within just a few days. Nanoscribe closes the gap between 3D printing and micro-optics with this flexible tool enabling unprecedented applications in micro-optics.
Examples of Micro-Optics fabricated by 3D Printing:
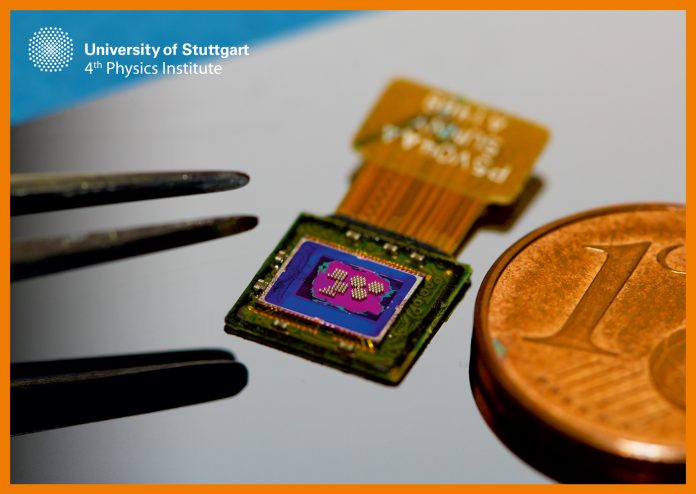
The freedom of design provided by 3D printing also implies that almost any concave or convex or entirely freeform surface shape can be fabricated with this technique. Recently, e.g., researchers from the University of Stuttgart (Germany) directly 3D printed doublet lens systems onto CMOS image sensors thereby creating a high-performance and compact imaging system. Not only the optical performance is impressive, but the design iteration process was drastically accelerated. It took less than a day to implement new designs from the idea to the final part.
A further outstanding structure demonstrating the high shape accuracy and optically smooth surfaces achievable by using this technology are the hemispherical micro-lenses (right). They have a shape accuracy better than 1 µm and a surface roughness better than 10 nm Ra. The array with a size of 1 square centimeter in total and semispheres with a height of 150 µm was written into a solid negative tone resist. Due to the optimized combination of hardware and software components one can achieve a high and consistent precision on the whole area of the writing field. Micro-optical components on wafer-level can be fabricated by the same technology.
Using a Nanoscribe system, the fabrication of diffractive optical elements (DOE) which typically have significantly smaller feature sizes than refractive optics, is possible as well. DOEs can be designed for functionalities that are hardly accessible with refractive optics, such as the generation of almost arbitrary light distributions in the far-field. By means of a Photonic Professional GT, functional multilayered diffractive optical elements (Image 4) can be directly patterned onto glass substrates enabling rapid protoyping and design iterations within a few days.
For more information, please feel free to download our new application note Micro-Optics.