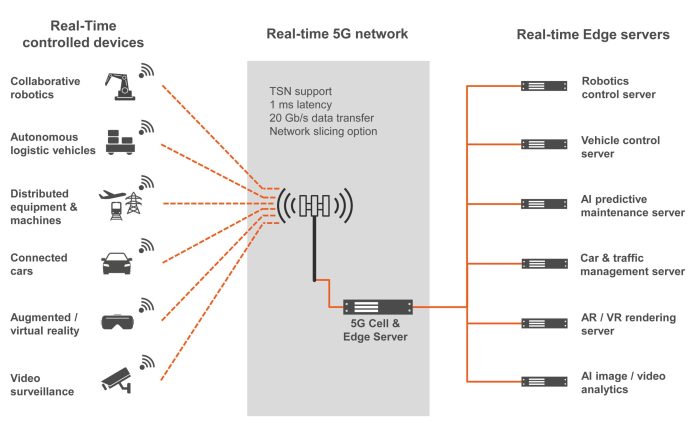
Real-time capable 5G cells with integrated edge servers are a key enabling technology for digital transformation, opening a plethora of new opportunities for IIoT, Industry 4.0 and critical infrastructure applications. However, to be able to process data in real-time and with low latency in harsh factory and outdoor environments such solutions need to be specially hardened. For this purpose, the world’s first COM-HPC Server-on-Modules that are designed for operation outside air-conditioned data centers are now being launched into the industrial field.
Digital transformation in industrial manufacturing requires fast real-time networks, yet laying cables everywhere is not always possible. The real-time capable 5G standard is therefore a real revolution for industrial communication as it enables reliable wireless distribution and processing of massive amounts of data in real time and, importantly, over longer distances than with WLAN. And since both stationary and mobile devices can use the 5G network, connecting entire factories becomes possible. For such use cases, 5G can manage a large density of networked devices and offers short response and latency times in the millisecond range. With network slicing, 5G also opens the possibility of creating independent virtual networks that are logically separated by a single physical network. Finally, 5G also provides the foundation for the introduction of cloud-native architectures which, with 5G-based edge computing, become real-time capable fog servers that can communicate wirelessly with all kinds of devices.
Private 5G infrastructures for business-critical applications
The opening of the 3.7 to 3.8 GHz frequency range to private mobile networks means that 5G can be used and privately operated by a wide variety of campus networks in Industry 4.0 environments and critical infrastructures in many other industries. The scalability of these private infrastructures and the compatibility of 5G with previous mobile communications standards, which can also be expected for future generations, also offer high investment security. More and more companies are therefore establishing their own private, on-premises 5G networks to run business-critical applications and to digitize production – a trend that is expected to intensify in the coming years according to a recent study by MarketsandMarkets.
Of course, companies can also use public networks. However, in rural areas where the public base station (aka macro cell) uses the 700 MHz band to achieve ranges of 15-20 km, the data rate is limited to 100 to 200 megabits per second. While this is enough for a large automotive plant to supply an entire factory site – which in the case of VW in Wolfsburg covers more than 6 square kilometers – with a single 5G cell, the available bandwidth is not sufficient for a fully connected factory. This would require the full bandwidth of the 5G data throughput capacity, which is why companies want to build their own campus networks. The 3.7 to 3.8 GHz frequency of such networks allows maximum upstream speeds of 100 to 200 Mbit/s and download speeds of 200 to 1000 Mbit/s. However, the cell range is limited to somewhere between 300 meters and 3 kilometers with a direct line-of-sight. Plants therefore require more than one cell. These are often highly compact so-called small cells or femtocells. Small cells are about the size of a pizza box. Without integrated edge server technology, the even smaller femtocells are about the size of a paperback and available for private purchase.
Robust 5G edge server technology opens new performance dimensions
In such installations, the edge server infrastructure behind the 5G microcells should ideally be provided directly in or at the base station/RAN (Radio Access Network) infrastructure by deploying VNF (Virtual Network Functions). Although other deployment scenarios elsewhere in the infrastructure, such as in micro data centers, are also possible provided the latency requirements are met. The advantage of a shared hardware platform is that both cloud edge server functionality and network function virtualization (NFV) can be deployed together in the centralized unit (CU).
The cells require integration of all necessary hardware to generate and process the 5G signals. This forms the physical interface between the 5G radio network and the digital baseband. In addition, the server performance required for the individual edge server functions also needs integrating. Since functions can vary from application to application, a modular design approach using Server-on-Modules is recommended. In this case, the application-specific functions can be realized on the carrier board – including, for example, implementation of the 5G radio logic with appropriate expansion modules. With Server-on-Modules based on the new PICMG COM-HPC standard and featuring the new Intel Xeon D processors, developers can gain access to a performance class that was previously unattainable for harsh environments. These rugged modules can be operated in the extended temperature range from -40°C to +85°C, are designed for long-term availability, and offer special protection against electromagnetic interference as well as shocks and vibrations.
To provide the necessary performance, the modules feature up to 20 cores, up to 1 TB of memory on up to 8 DRAM sockets at 2933MT/s, up to 47 PCIe lanes per module in total and 32 PCIe Gen 4 lanes with double throughput per lane, as well as up to 100 GbE connectivity and support for time-coordinated computing (TCC) and time-sensitive networking (TSN) to enable real-time communication between devices. Further significant performance increases are expected in the future with the release of new modules. However, the performance available today is entirely sufficient for current campus network designs with Open-RAN solutions using a total of 5 server processors for the backhaul packet core and the midhaul CU/DU servers. These, however, require rack air conditioning and cannot be used in the extended temperature range. By consolidating these functions into a single microcell, it becomes conceivable to implement less performant but real-time capable small 5G cells on only two virtualized modules.
Deterministic real-time with cloud native virtualization
However, to be able to run different real-time applications independently on just one edge server, you also need server balancing and server consolidation services. Both are required as well for the platform-side support of real-time-capable virtual machines, which provide the server functionality for the communication needs of 5G subscribers. The real-time hypervisor from Real-Time Systems is ideal for this purpose, for example. Such virtualization enables enterprises to use their private 5G networks for heterogeneous real-time applications hosted on a single server platform by utilizing network slicing. This then allows them to allocate dedicated system resources to individual tasks and processes to ensure determinism. Server-on-Modules from congatec are designed for such use cases and can be quickly modified to include the necessary parameterizations for real-time collocation services, where different applications share resources. This allows factory operators to provision real-time capable 5G edge data servers more efficiently for services such as machine automation, robot control or automated logistics in their manufacturing facilities.
Another advantage of the new modules is that they already integrate TSN natively in the processor module. If the 5G core logic also supports TSN, the modules enable standardized data exchange and continuous, transparent communication from the sensor to the cloud, for example using OPC UA as an open real-time communication protocol. The 5G Alliance for Connected Industries and Automation (5G-ACIA), a working group of the leading German manufacturers association ZVEI, is developing the necessary specifications for QoS, network security and, above all, TSN integration. This should even enable jitter-free isochronous real-time, where communication cycle times are precisely clocked and can be synchronized in both directions from 100µs to 2ms.
In the future, the COM-HPC specification will be extended to include functional safety. Modules supporting this functionality could then be used as central controllers for autonomous intralogistics vehicles such as tow tugs, unit load carriers, forklifts, assembly line vehicles or pallet trucks, or to orchestrate collaborative robots. This will make it possible to provide pre-certified computer modules that make it easier and faster for customers to realize new safety applications.
The all-in-one solution: COM-HPC Server-on-Modules for 5G microcells
The new COM-HPC Server-on-Modules revolutionize edge server design in three respects: Rugged server designs featuring the new Intel Xeon D processors can be implemented in the microcells of private 5G networks without additional air conditioning. This as well as support for the extended temperature range makes the new designs suitable for use beyond standard industrial environments, including outdoor and mobile applications in the construction industry or agriculture. The world’s first COM-HPC Server-on-Modules from congatec provide significantly improved performance and scalability, offering massively higher memory bandwidth with up to 20 cores and up to 8 DRAM sockets. Besides this industry first, they also enable deterministic real-time in the industrial IoT. This makes them the ideal basis for building customized 5G cells with integrated edge server technology as an all-in-one solution.
For 5G network administrators, the new modules also offer a set of high-quality, application-specific server features: For business-critical designs, these include powerful hardware security features such as Intel Boot Guard, Intel Total Memory Encryption – Multi-Tenant (Intel TME-MT) and Intel Software Guard Extensions (Intel SGX). Comprehensive remote application server (RAS) functionalities support remote hardware management functions such as IPMI and Redfish, for which there is also a PICMG specification that ensures the interoperability of such implementations. Lastly, congatec also provides comprehensive services to help with individual system developments and customer-specific implementations. These services range from COM-HPC design training to personal integration support and compliance testing of customer-specific carrier board designs.
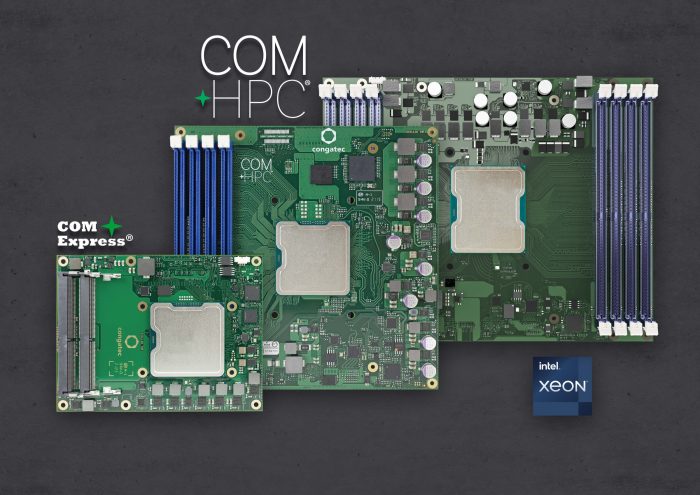
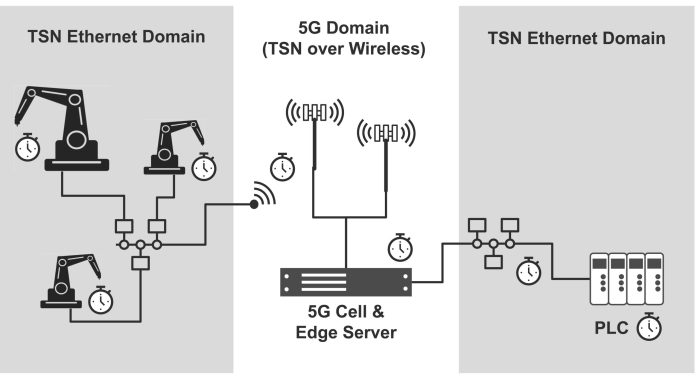
 Caption 1: Industrial 5G cells can have extremely diverse tasks. Server-on-Modules, which make 5G network and edge computing performance scalable, enable OEMs to cost efficiently scale the performance of small cells that are barely larger than a pizza box.
Caption 1: Industrial 5G cells can have extremely diverse tasks. Server-on-Modules, which make 5G network and edge computing performance scalable, enable OEMs to cost efficiently scale the performance of small cells that are barely larger than a pizza box.
Caption 2: If 5G cells support TSN, they can host real-time applications.
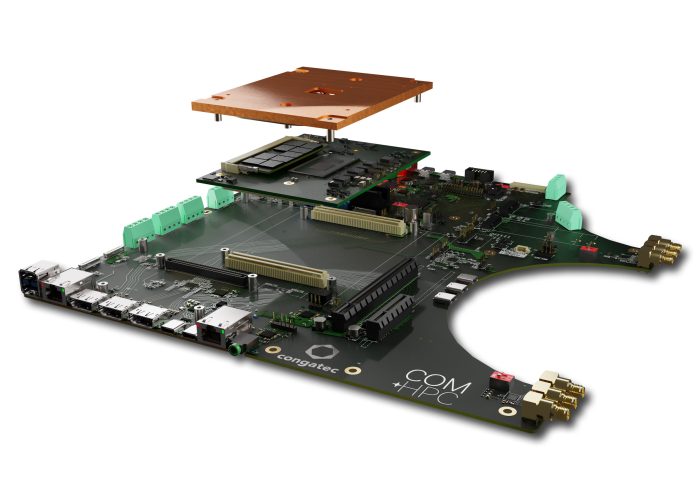 Caption 3: Custom carrier boards can even be designed for 5G cells in lamp posts.
Caption 3: Custom carrier boards can even be designed for 5G cells in lamp posts.
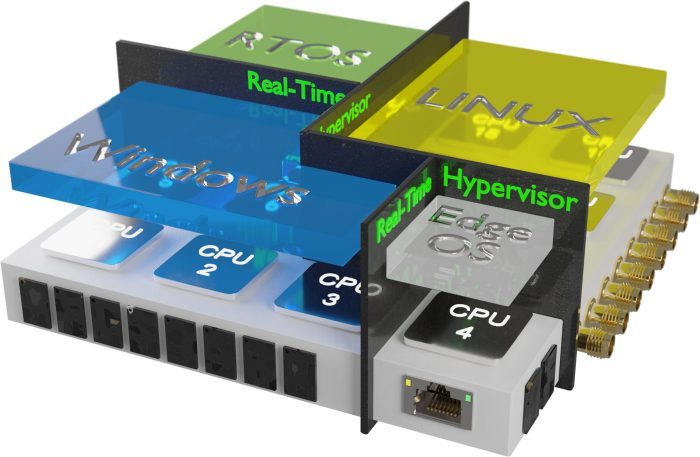 Caption 4: Server consolidation at the industrial 5G edge: Up to 20 cores can host a variety of 5G NVF and industrial real-time applications.
Caption 4: Server consolidation at the industrial 5G edge: Up to 20 cores can host a variety of 5G NVF and industrial real-time applications.
Available now: Server-on-Modules with Intel Xeon D
Application-ready samples of the below Server-on-Modules are now available, including suitable rugged cooling solutions for the given processor TDP. On the software side, the new modules come with comprehensive board support packages for Windows, Linux and VxWorks, as well as the RTS hypervisor. Supported high core count (HCC) and low core count (LCC) flavors of the Intel Xeon D processor series include:
HCC variants
The COM-HPC Server Size E modules (conga-HPC/sILH) are offered in 5 different Intel Xeon D 27xx HCC processor variants with a choice of 4 to 20 cores, 8 DIMM sockets for up to 1 TByte of 2933 MT/s fast DDR4 memory with ECC, 32x PCIe Gen 4 and 16x PCIe Gen 3, and 100 GbE throughput plus real-time 2.5 Gbit/s Ethernet with TSN/TCC support at a processor base power of 65-118 Watt.
LCC variants
The new COM-HPC Server Size D modules as well as the traditional COM Express Type 7 modules come with 5 different Intel Xeon D 17xx LCC processors with a choice of 4 to 10 cores. While the conga‑B7Xl COM Express Server-on-Modules support up to 128 GB DDR4 2666 MT/s RAM on up to 4 SODIMM sockets, the conga-HPC/SILL COM-HPC Server Size D module offers 4 DIMM sockets for up to 256 GB 2933 MT/s DDR4 RAM or 128 GB with ECC UDIMM RAM. Both module families offer 16x PCIe Gen 4 and 16x PCIe Gen 3 lanes. For fast networking, they provide up to 50 GbE throughput and TSN/TCC support via 2.5 Gbit/s Ethernet and 40‑67 Watt processor power.
Author Article by: