Authors: Anand Kannan, Senior Manager Product Marketing, Infineon and Alexander Guba, Program Manager, Arrow Electronics
The USB Power Delivery (PD) standard continues to evolve. The most recent USB PD 3.2 specification now supports sourcing and sinking up to 240 W (48 V, 5 A). This article will discuss the main trends in USB PD and explore why implementing USB-C in 2024 is no longer considered an innovation, but a good approach to staying competitive with new designs. Finally, the article will provide an overview of a source and sink solution that supports 240 W using Infineon’s primary- and secondary-side controllers, EZ-PD™ PMG1 high voltage microcontrollers with integrated USB-C PD and Infineon’s CoolGaN™ power transistors.
USB is currently a well-recognised set of standards in consumer and automotive applications and is rapidly expanding into the industrial and e-mobility sectors. Starting with the first official USB 1.0 revision in 1996, which supported up to 1.5 Mbps data transfer and up to 2.5 W of power, it has evolved to support an incredible 80 Gbps and 240 W through a single USB-C cable. Nevertheless, about half of all of Arrow’s booth visitors at a recent show, were surprised to learn that USB standards already support 240 W.
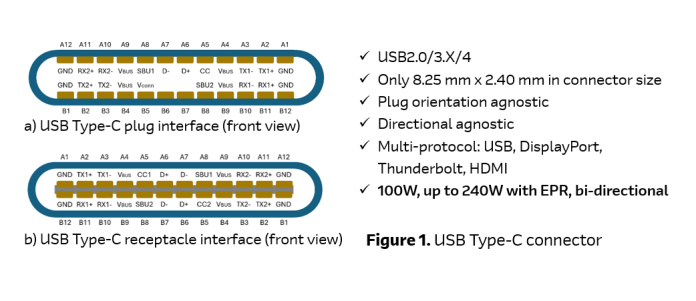
USB Type-C connector
Let’s dive deeper into the details of the USB Type-C standard connector. The big advantage of this connector is that the interface is plug-agnostic due to its symmetrical design – it functions regardless of which way it is connected. This connector supports power delivery up to 240 W and accommodates protocols like HDMI, DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, and others through its Alternate Mode, known as Alt Mode. These features together have had significant influence on the industry.
Looking at the connector pins, shown in Figure 1, the CC1 and CC2 pins – known as cable configuration pins – are used to control the orientation and determine their roles: Downstream Facing Port (DFP) for the source power role, Upstream Facing Port (UFP) for the sink role, and Dual-Role Port (DRP) for both source and sink roles. Another function of the CC pins is to facilitate data transfer when negotiating Power Delivery contracts between the source and sink.
Four differential pairs labelled RX/TX for USB 5 Gbps or higher speeds, were used starting with USB 3.1. These lines operate in full duplex mode, while the two pairs of legacy pins, D+/D-, located in the centre, operate in half duplex mode. Pins labelled as SBU, or SideBand Use, are utilised for Alt Modes, such as enabling video output for DisplayPort or Thunderbolt. The VBUS pins are used to deliver power up to 240 W. All four external ground (GND) pins are intended for grounding. Proper grounding is essential for USB-C at high data rates and in cases of high-power delivery over the connector.
USB Power Delivery specification
Taking a deep dive into the USB Power Delivery standard, as mentioned earlier, the initial versions of the USB standard allowed the maximum power of 2.5 W (5 V@500mA) over VBUS. With USB 3.0, this increased slightly to 4.5 W (5 V@900mA), but it was still not sufficient for many applications.
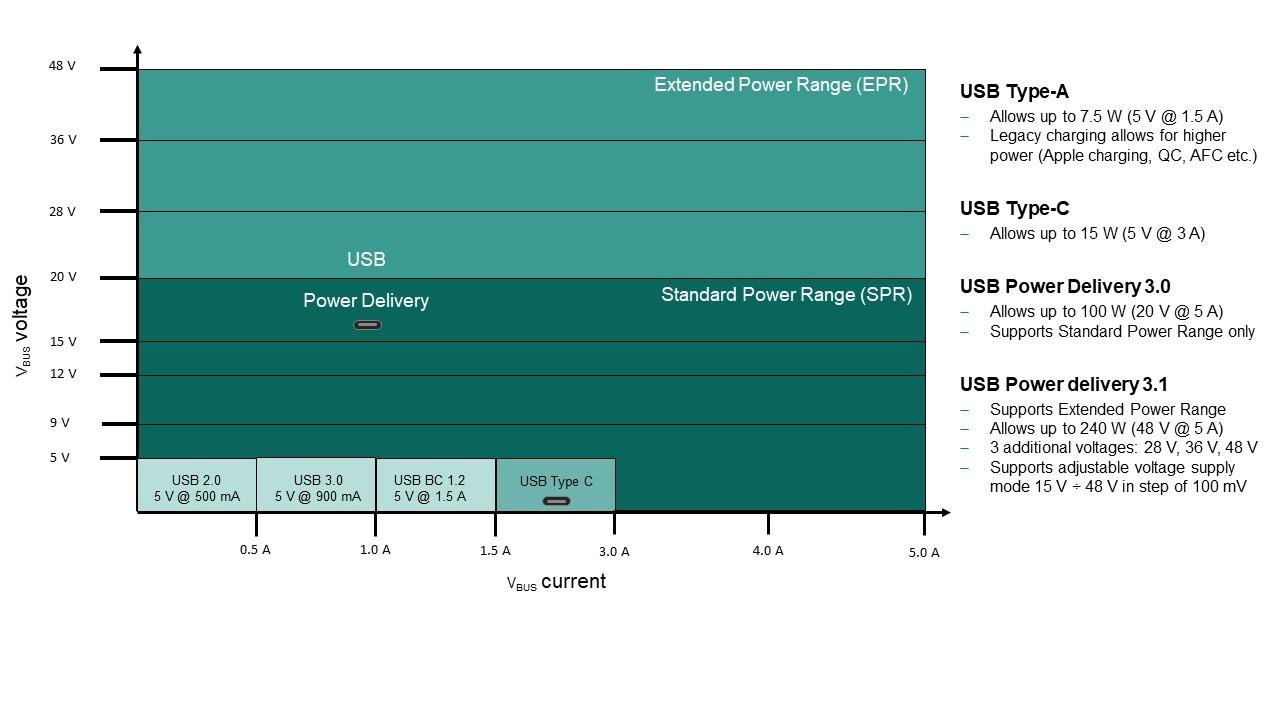
With the introduction of USB Type-C and Power Delivery in 2014, the USB power capabilities were significantly increased. By default, with the means of the USB Type-C, the maximum power available increased to 15 W (5V@3A). With the full implementation of the USB PD, it became possible to deliver up to 100 W (20V@5A) from a single USB source.
Starting from the USB Power Delivery 3.1, the specification allows for up to 240 W (48V@5A). All voltage levels higher than 20 V are now categorised as Extended Power Range (EPR). The specification also includes support for an Adjustable Voltage Supply (AVS) mode, which allows the voltage to be adjusted in steps of 100 mV for voltages above 15 V.
Market trends evolution
USB is an almost 30-year-old standard, but the most significant improvements in speed and power capabilities were observed just recently. Over the last eight years, USB-C has been adopted by mainstream device manufacturers, such as laptop and smartphone makers.
Now, most laptops feature at least one USB-C port. Additionally, many other mobile devices have switched to USB-C, alongside a noticeable increase in USB-C power adapters on the market. Simultaneously, automotive manufacturers have added more USB-C ports in their vehicles to offer enhanced charging options for drivers and passengers. Following this trend, the adoption of USB-C in the embedded and industrial sectors is expected to increase significantly in the next few years.
The vision for 2025 and beyond is that many electronic devices, currently powered at up to 240 W, will adopt USB-C as a standard port for data communications and charging.
Among the key factors further driving USB adoption are the race in battery technologies, the shift to industrial applications, and the increasing worldwide acceptance of USB. Local regulations will also have a significant impact: USB Type-C and USB PD will become mandatory across all European Union countries for many applications by the end of 2024. Similar discussions are currently underway in the USA and other countries.
Following these trends nowadays isn’t just about staying at the cutting edge of technology — it has become an important competitive feature that secures a position in the market. But what are the main advantages of the technology driving such rapid adoption of the standard in recent years?
Key technology drivers
Combined data and power capability: one of the most important drivers of USB-C’s fast growth is its ability to transmit high-speed data, video, and power through a single, slim connector. This feature enables the design of smaller and thinner devices.
Unification and reuse advantage: Traditional power adapters come with fixed voltage and current levels and often feature unique barrel connectors, which means they can only be used with their intended device. Such adapters are often not compatible with other devices.
In contrast, USB-C power adapters are universally compatible, offering a USB Type-C connector that works across many devices. Moreover, with the 240 W USB PD adapter, it is possible to negotiate voltages and currents up to 240 W (48 V @5 A). This enables charging any USB device up to 240 W, including 5 V or 15 V devices, 45 W phones, and 160 W laptops. Even your future devices, e.g. power tool, e-Bike or consumer 3D printer could be potentially charged using the same adapter. A single USB power adapter can be used to charge many devices, thereby saving costs for consumers.
Saving R&D and manufacturing costs: customized power supplies, whether integrated or using a customized connector, often require additional investments in design, manufacturing, and testing, especially when production quantities are not very high.
Adoption of USB-C power adapter instead of a custom power supply along with appropriate Infineon USB-C PD controller to sink power will help to decrease the cost per watt ratio. This will naturally happen due to the huge competition among chargers’ manufacturers on the mass market.
Improving time-to-market: in addition to the higher costs for the external or embedded charger design, customized solutions often require much more time for R&D and further tests. While the simple sink USB implementation along with the certified USB charger enables faster time to market in most of application cases.
Reducing dependence from OEMs: another situation arises when the power supply or integrated AC/DC power module comes from an OEM manufacturer. In this case, the future of the project may highly depend on the third- party’s manufacturing plans. Once the USB sink function is implemented, all certified USB adapters with similar power capabilities from the consumer market could be used, thus reducing dependence on a single OEM supplier.
E-waste reduction: at first glance, it may not be evident, but the unification of chargers has a significant impact on environmental protection. While each individual charger is small, the environmental consequences are substantial when considering the millions of chargers discarded each year.
Improving brand perception: the fact that the design company keeps up with trends always adds additional appeal to your potential customers. Imagine how you would feel if your company bought modern and expensive measurement equipment that came with a CD for installing drivers and the software tools.
USB Type-C connector: besides all the USB driving factors and advantages mentioned previously, the most important feature itself was the introduction of the 24-pin USB Type-C connector in 2014 (see Figure 1).
240 W USB PD sink reference design
Following the latest trends in the industry, Arrow and Infineon introduced the new 240 W PD 3.1 sink reference design using Infineon’s EZ-PD™ PMG1-S3 high voltage microcontroller intended to support high power USB applications. The new reference design supports up to 48V@5. A Power Delivery Object (PDO) sink mode, which is the highest level achievable with the latest USB PD standards.
The reference design further extends the existing power sink capabilities of Infineon’s EZ-PD™ PMG1 family of high-voltage microcontrollers from 140 W to 240 W, which is important for many power-demanding and fast-charging applications.
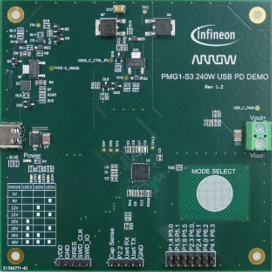
This 240 W sink reference design board REF_ARIF240WS3, shown in Figure 4, complements the recently released Infineon’s USB PD 3.1 source evaluation board REF_XDPS2222_240W1. This combination enables engineers to be among the first on the market with a complete 240 W USB PD 3.1 source-sink solution.
Infineon’s 240 W USB PD source reference design
The complementary design for 240 W power source, Infineon’s REF_XDPS2222_240W1 based on CoolGaN™ technology, is a high efficiency form-factor USB PD 3.1 reference design, with 25 W/in³ power density, using the XDP™ digital power XDPS2222 PFC + hybrid flyback (HFB) combo IC (Figure 5).
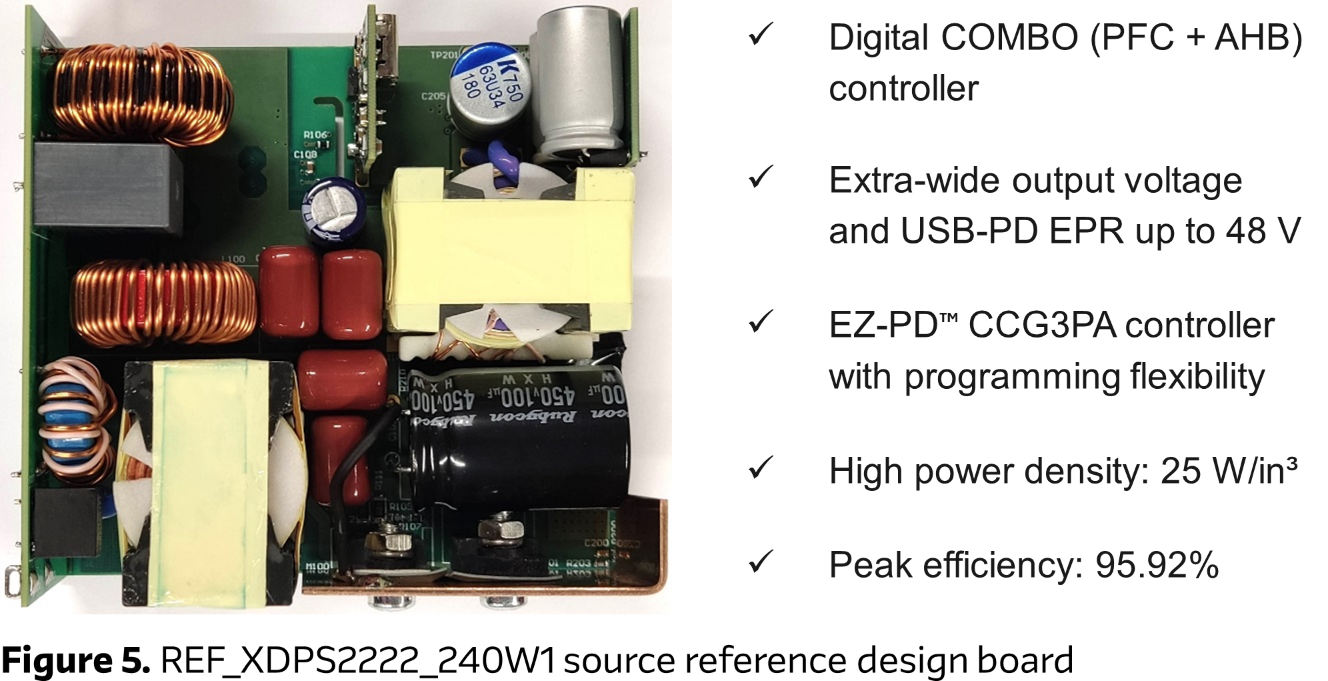
The internal handshaking between the PFC and HFB controller and the adaptive bus voltage setting make the XDP™ XDPS2222 controller perfect for applications with wide AC input and very wide output voltage range, such as USB PD extended power range (EPR) adapters and battery chargers. The main features, include HFB ZVS high- and low-side operation, fast response HFB peak current control, harmonised PFC and HFB operations, pulse skipping at light loads, automatic PFC enable/disable control, and self-adjusting PFC bus voltage level.
These reference designs are intended to support a broad range of applications, like light electric vehicles (e-bikes, e-scooters and other personal e-mobility devices), drones, mobile robots, 3D printers, professional AV equipment, power tools, medical equipment, home appliances, home entertainment devices, and more.
But generally, any application requiring 0 to 240 W could benefit from adopting USB-C for power, and the outstanding features of USB PD provided by these advanced designs.
Supporting services
Both reference designs are available on request. In addition to technical support, Arrow offers a range of technical support services, including schematic customisation and PCB modifications, helping to maximise the potential of customers’ designs and reduce time-to-market. Scan the below QR Code, for more information.