Advancements in ultrasound imaging technology, along with rising demand for minimally invasive diagnostics and therapeutics, have made it possible to implement ultrasound applications for medical use. For example, employing ultrasound for remote patient monitoring has become increasingly popular given its cost-effective, safe, and fast diagnostic capabilities. There is also demand for ultrasound devices to become more portable so that high-quality medical care can be consistently given anywhere from a hospital or doctor’s office to someone’s home or a remote village. In this article, I’ll examine compact battery charger integrated circuits (ICs) and solutions for ultrasound point-of-care products that are used by medical professionals to diagnose problems wherever a patient is receiving treatment.
Types of point-of-care ultrasound devices and charging requirements
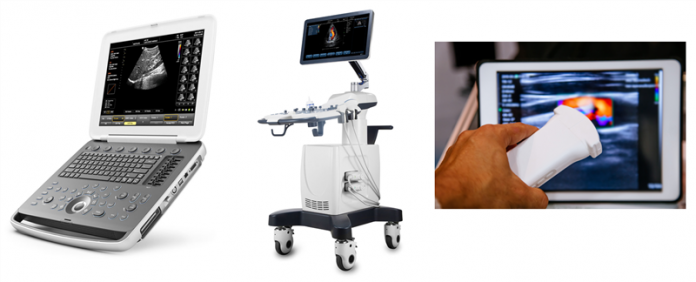
There are three major types of ultrasound devices: cart-based, notebook, and handheld. System power consumption varies among the three. As a result, they need different battery configurations.
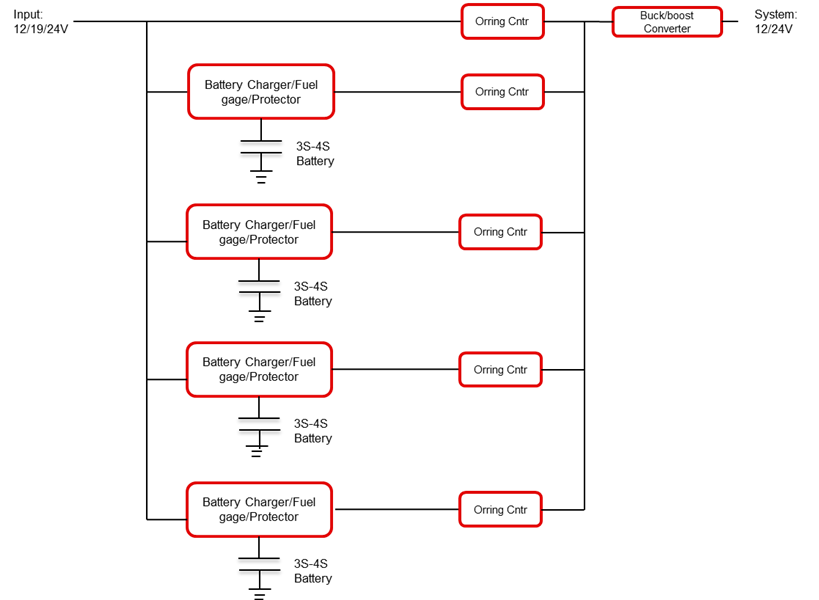
As shown in Figure 1, a cart-based ultrasound machine is the most powerful of the three types. The maximum system current can be as high as 20 A at 12 V. The cart typically includes four individual battery packs connected in parallel to supply the system load sufficiently. Each battery charger pack is configured with four or more cells in series.
Because of air traffic control regulations on lithium-based batteries, the capacitance of each battery pack cannot exceed 100 watt-hours. As a result, the four battery packs cannot be tied directly together. Each individual pack needs its own charging and discharging path, as illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 1: Point-of-care ultrasound devices (cart-based, notebook, and handheld)
Figure 2: A simplified multi-battery pack battery-management system
Notebook-based devices also have a maximum battery capacity limitation of 100 watt-hours. System power consumption of an ultrasound notebook can go as high as 10 A at 12 V. Therefore, this type of machine typically includes two individual battery packs with separate charge and discharge paths.