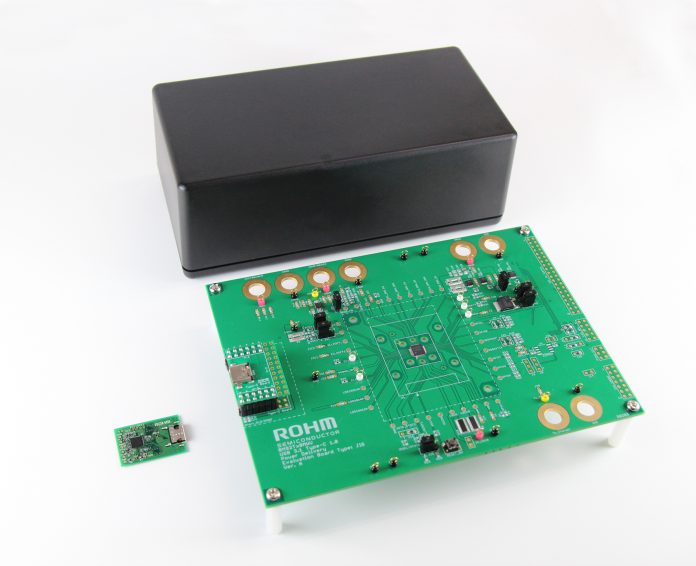
ROHM has recently announced the availability of USB Power Delivery (USBPD) compatible transmitter/receiver evaluation boards designed to connect to information and peripheral devices using the new ‘Type-C connector’.
Recent years have seen a greater demand to reduce industrial waste in many regions, including Europe, for example by utilizing or developing universal connectors and chargers for a variety of electronic devices that can be used worldwide. As such, the new USB Type-C connector and USB Power Delivery standard developed by the USB Implementers Forum are attracting increased attention, featuring a breakthrough interface that boasts a compact, reversible/flippable connector capable of simultaneously transmitting data and scalable power over a wide range.
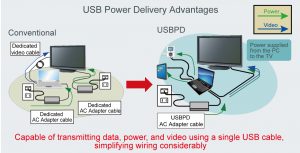
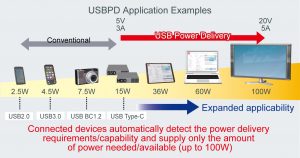
USBPD extends the power supply range from the conventional 15W to up to 100W (20V/5A) between USB Type-C compliant devices. This enables larger devices such as laptops and TVs to be powered via USB while contributing to the transformation of infrastructure as the number of USB ports in homes and hotels continues to grow.
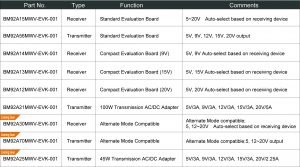
The new BM92AxxMWV-EVK-01 series integrates ROHM’s USBPD controller IC that supports the USB Type-C Rev1.1 and USBPD Rev2.0 standards for connecting with USB Type-C™ devices. ROHM leveraged leading BiCDMOS processes and circuit technology to develop USB PD controller ICs that are expected to provide greater convenience while significantly reducing industrial waste. The initial launch will consist of six boards in a mix of both receiver and transmitter types to meet the needs of a variety of applications. Users can combine receiver and transmitter boards to easily achieve and evaluate USB PD operation.
The boards were being offered from the end of April/2017 through online distributors RS Components, Chip One Stop, Zaiko Store (Core Staff), with all necessary supporting materials available on ROHM’s website.
USB PD Application Examples
Launch Date: June 2017



What is USB Power Delivery?
A USB power expansion standard for delivering up to 100W of power over USB. This allows larger devices such as laptops to be powered that are not possible using conventional USB while speeding up charging time considerably for portables. Under the USB PD protocol connected devices negotiate power requirements and enter into a contract to determine the optimum voltage and current levels needed. USB PD communication requires a new dedicated CC line that functions independently of conventional USB data transmission.
Terminology
USB Type-C Standard (Type-C Connector)
USB Type-C is a new receptacle (concave connector), plug (convex connector), and cable standard defined under USB3.1. Unlike conventional USB, it features a more compact, reversible, flippable connector design that can be used without distinguishing between Host and Device sides.
USB Implementers Forum, Inc. (USB-IF)
A standards organization established in 1995 to promote the creation, management, and adoption of USB standards. USB-IF currently has more than 800 member companies.
Alternate Mode
A control mode that can also handle video signals, eliminating the need for a dedicated video terminal required for electronic devices such as laptops. This makes it possible to transmit data, power, and video signals over a single USB cable, significantly reducing waste while providing greater convenience.







