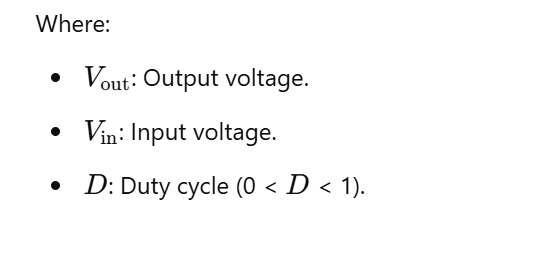DC-to-DC converters are electronic devices that change one DC voltage level to another. They are widely used in power supplies for electronic devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems. Here are the main types:
- Linear Regulators:
- Simple and cost-effective.
- Converts excess voltage into heat, making them inefficient for large voltage differences.
- Example: Low Dropout Regulators (LDO).
- Switching Converters:
- Efficient and suitable for large voltage differences.
- Types:
- Buck Converter (Step-Down):
- Reduces input voltage to a lower output voltage.
- Boost Converter (Step-Up):
- Increases input voltage to a higher output voltage.
- Buck-Boost Converter:
- Can increase or decrease voltage depending on the configuration.
- Cuk Converter:
- Provides an inverted output voltage and regulates it.
- SEPIC (Single-Ended Primary Inductor Converter):
- Allows for voltage output either higher or lower than the input.
- Flyback Converter:
- Common in isolated power supplies for low-power applications.
- Push-Pull Converter:
- Symmetrical design for higher power and efficient isolation.
- Buck Converter (Step-Down):
- Charge Pump Converters:
- Use capacitors for energy storage and voltage conversion.
- Lightweight and efficient for low-power applications.
- Isolated Converters:
- Separate the input and output using transformers or optocouplers for safety.
- Examples: Flyback and Forward Converters.
DC-to-DC Conversion Formula
The power balance principle is used to derive relationships in DC-to-DC converters. The formulas vary based on the converter type:
DC-to-DC Converter Examples
- Consumer Electronics:
- USB power adapters using buck converters to step down 12V to 5V.
- Automotive:
- Electric vehicles use DC-DC converters for powering 12V systems from a high-voltage battery pack (e.g., 400V or 800V).
- Renewable Energy:
- Solar power systems employ boost converters to increase panel voltage for battery charging.
- Data Centers:
- Intermediate bus architectures use isolated converters to step down 48V to server-operable voltages (e.g., 12V or 5V).
- Industrial:
- Power supplies for robotics and sensors using isolated flyback converters for safety.