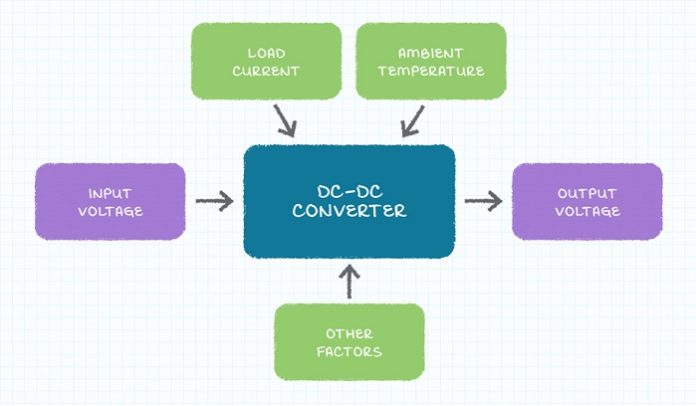
As with most power supplies, a primary consideration when selecting a DC-DC converter is to determine the output load power requirements of the system. The output requirements of the DC-DC converter include the output voltage and current supplied by the converter. The output voltage may have tolerance specifications dependent upon environmental conditions such as input voltage, output load current, ambient temperature, etc. The load current requirement specifications should include the minimum, maximum and typical values.
Requirement specifications for DC-DC converter applications are unique compared to AC-DC supplies in that input voltages are not standardized, as they are for ac-dc power supplies. When selecting a dc-dc converter, it is necessary to specify the range of input voltages that will be applied to the converter.
Isolated vs. Non-isolated Configurations
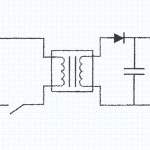
DC-DC converters are available in either isolated or non-isolated configurations. Isolated converters are constructed with the input and output circuits galvanically isolated; there is no dc path between the input and output. These converters are often used to separate the input and output circuits for either electrical noise or dangerous voltage isolation. Isolated converters are available with multiple output voltages from a single converter.
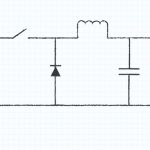
Non-isolated converters have a dc connection between the input and output through the common ground between the input and output circuits. This class of converters can be made smaller and less expensive than isolated converters. Some non-isolated converters are capable of producing a negative output voltage from a positive input voltage.
Regulated vs. Unregulated Output Voltage
Most DC-DC converters produce a tightly regulated output voltage, similar to ac-dc supplies. Smaller or less expensive converters can be used in applications that can tolerate an unregulated output voltage. The selection of a regulated or unregulated output voltage is often available only on low-power converters.
Package and Mounting Choices
DC-DC converters are available in a variety of package and mounting styles. In applications where the converter will be mounted directly onto a PCB, there are choices of surface mounting (SMT) or through-hole mounting (THM), as well as a single in-line pin (SIP) or dual in-line pin (DIP) configurations. Chassis-mounted converters are available for applications requiring that style of mounting. Many converters are available in DIN rail mount configurations for industrial applications. Both open frame and encapsulated converters can be found in the most package and mounting configurations.
EMI and EMC Concerns
Most electronic products offered for sale are required to meet EMI and EMC (Electromagnetic Interference and Electromagnetic Compatibility) regulatory requirements. The goals of the regulatory requirements are to ensure the products do not interfere with the operation of other products and that outside electrical noise does not prevent the certified products from operating correctly. Dc-dc converters can be certified to comply with regulatory requirements, but the completed system is certified in most applications, and the internal sub-circuits do not require certification.
Safety Requirements
Similar to EMI and EMC regulatory requirements, most electronic products sold are required to meet regulatory safety requirements. As with the EMI and EMC regulatory certification, products are granted safety certification for the final product, and certification is often not required for the internal sub-components but can be obtained if necessary. It should be noted that dc-dc converters sold in the EU and UK with input voltage ratings of 75 V or greater require safety certificates, be sure of your requirements for other geographic locations. Safety certifications for converters should also be obtained if the dc-dc converters are used for isolating users of products from hazardous voltages.
Additional Features
In addition to the characteristics of DC-DC converters discussed above, other features may be beneficial or required in product designs. Some converters allow the designer to adjust the output voltage with the use of external resistors. High-power converters often include load voltage sense terminals to enable the converter to compensate for voltage drops in the conductors between the converter’s output and the converter’s load. Including remote on-off capability allows the designer to enable or disable the output voltage from the converter with an electronic signal.
The choice of a suitable converter depends mainly on what device you are designing. If you want to design a small portable device, it is worth considering miniature converters. For larger equipment, you can use converters of bigger dimensions with a built-in heat sink to facilitate heat dissipation. Additionally, it is necessary to specify the type of converter needed – step-up, step-down or step-up/down. If you wish to minimise energy losses, it is worth equipping yourself with voltage converters of the highest possible efficiency. The standard efficiency of such devices falls within the range of 80-95%. Additionally, it is worth remembering about the basic parameters of the converter, such as: maximum output current, output voltage range and input voltage range.