Brian Condell and Michael Jackson | Analog Devices
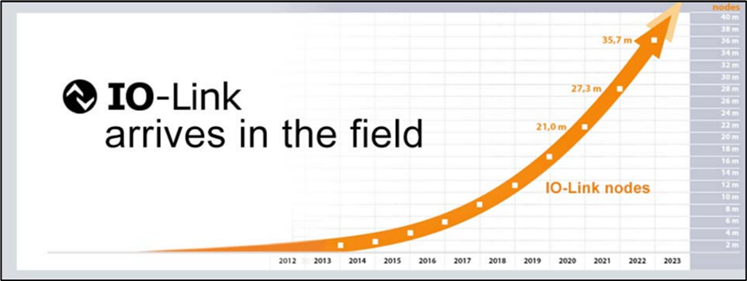
Industry 4.0 is about gathering data from the very edge of the factory floor to provide factory controllers with the valuable insights they need to make better informed or ‘smarter’ decisions. It also allows manufacturers to customize products quickly and easily without incurring substantial costs in reconfiguring their manufacturing processes. This opens the door to ‘batch-of-one’ manufacturing processes, which reduce waste and makes factory production more sustainable. IO-Link has a significant role to play in making Industry 4.0 real, not only for new factories but also by making it easy to upgrade existing brownfield facilities. The number of IO-Link nodes has been growing exponentially in recent years and this growth trajectory is projected to continue. This blog looks at the three key benefits that IO-Link delivers for manufacturers who want to be smarter about how they run their processes. Figure 1 below shows IO-Link growth rate.
IO-Link Brings Intelligence to the Edge
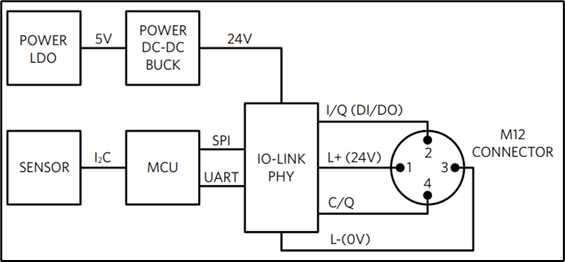
IO-Link provides sensors and actuators at the very edge of the factory floor with a bidirectional, digital data communications interface up to 230kbps. This enables them to measure, monitor, and influence potentially every stage of the production line. More decision-making at the edge means less data requires transferring to a PLC in the control room, saving time and energy. For example, by using pin 2 (I/Q) in the IO-Link interface as a digital output (DO), in addition to the C/Q data line, a sensor can read the input signal from a binary sensor and simultaneously drive an LED to flag that a threshold has been exceeded with no requirement for user input in making this decision. Figure 1 below shows the block diagram of a typical IO-Link Sensor.
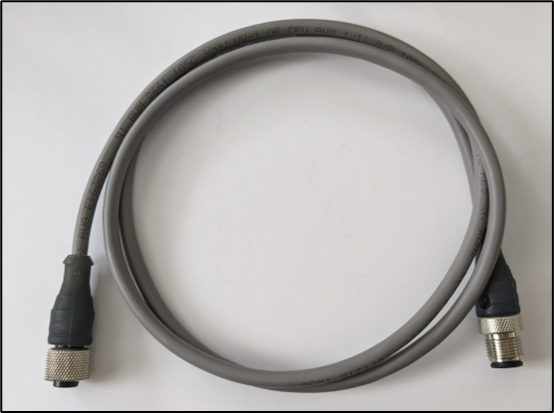
IO-Link Simplifies Installation
IO-Link uses a standardized interface that replaces traditional analog, binary, and serial interfaces with a convenient M12 connector already commonly in use in industrial environments. Additionally, upgrading a facility to use IO-Link is low-cost because it uses standard unshielded cabling installations like the 3-core, unshielded IO-Link cable with M12 connectors shown in Figure 3. IO-Link is also backward-compatible with serial input/output (SIO) binary signaling, meaning IO-Link capable sensors can communicate with existing PLCs using a standard digital input communication channel. Once a PLC module has been upgraded to connect with an IO-Link master, the C/Q line on an IO-Link channel enables bidirectional communication to take place with devices on the factory floor. IO-Link is also fieldbus agnostic meaning it can be used seamlessly in a variety of industrial networking architectures.

IO-Link Reduces Maintenance and Increases Uptime
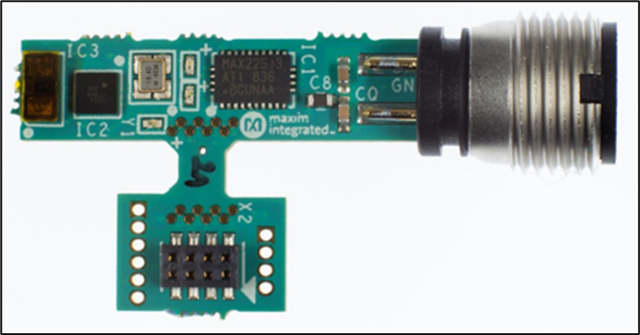
IO-Link enables the flow of real-time diagnostic information that allows engineers to identify and quickly address problems before they cause a process to go down and allowing technicians to replace faulty sensors quickly. Self-commissioning devices and automatic parameter setting is a feature of IO-Link capable devices which makes this task even easier. In many cases, technicians no longer need to visit the factory floor at all, as configuration updates can be performed remotely from the control room. For example, when a production line needs to be adjusted for a different product, process parameters can be reconfigured in real-time, minimizing downtime, and allowing a speedier return to full production. Figure 4 below shows a reference design for a distance sensor like those used to measure the size of objects on a conveyor belt. However, unlike conventional sensors, the measurement distance for this IO-Link sensor can be modified remotely from the process control if the tolerance for the object size required changing.