Many automotive, communication, and industrial systems take real-world input and provide corresponding outputs to create a precise control response. For example, autonomous driving detects and controls vehicles based on the real-world input of their proximity to other objects. In telecommunication radios or base stations, the outdoor temperature can affect power requirements for transmission, requiring amplification to produce the correct output. Industrial equipment makes real-time changes to protect factory flow, testing and
calibration.
Most of the components in these systems are increasingly moving toward digital technology, but the front ends of these systems – which provide precision and accuracy – remain mainly analog. Analog subsystems require reference voltages and currents to create a precision setpoint to bias a laser diode, command a motor position, or compare external signals. A stable reference is paramount to overall system accuracy, as references
can supply fixed voltages to many other components on a given board.
In this technical article, I’ll explore the key specifications of a precision digital-to-analog converter (DAC) that make it a suitable voltage reference for a design and explore the added benefit that the programmability of a DAC provides. These three specifications contribute to the stability and versatility of a DAC and help make DACs a good fit for a programmable voltage reference.
Provide accurate, stable programmable references for analog circuits.
Specification No. 1: output range
When selecting a DAC for use as a programmable reference, the output range is very important. It’s likely that you already know what voltage the reference needs to supply. Some DACs, like the DAC81404, can provide multiple ranges of output that are high voltage (>5 V), low voltage (≤5 V), bipolar (±5 V, ±10 V, ±20 V), and unipolar (spanning from 0 V to 40 V) outputs.
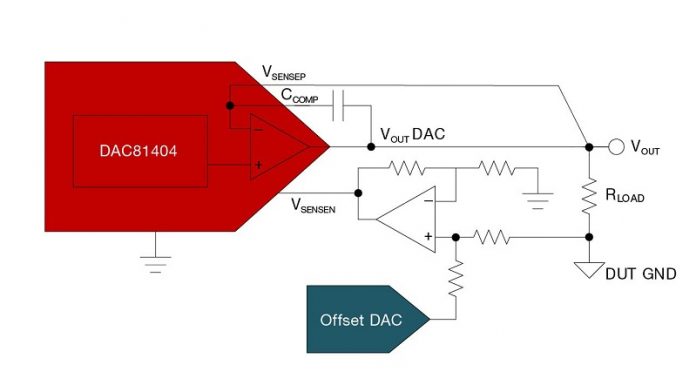
Figure 1 showcases a feature of the DAC81404 that enables it to sense a voltage drop on the load, R LOAD, that the DAC is driving, then shift the DAC’s output up or down depending on this drop to make sure the DAC’s output is the desired output at V OUT. This voltage drop can be compensated for from -12 V to +12 V. The V SENSE feature further contributes to the DAC’s output accuracy, thereby affecting overall system accuracy. The
circuit in Figure 1 also illustrates an interesting feature that would allow for asymmetric output ranges. For example, you could output – 3-V to +23-V output ranges from the DAC81404, made possible by the V SENSE feature.
Specification No. 2: Stability and drift over time
One of the most important qualities of a good reference is its stability over both time and temperature. Most semiconductor manufacturers specify drift over time in DAC data sheets; it’s usually called “output voltage drift over time.” What this specification describes is the DAC’s ability to hold an output voltage across the full- scale range of the DAC or the full-scale range at a given temperature (40°C) for some given time (usually 1,000
hours). Using the DAC81404 as the example once again, in this screenshot from its datasheet (Figure 2), you can see that it’s specified with the same criteria and boasts a low drift of ±6 ppm across the full-scale range.
DAC81404 also has a precision internal reference that provides a maximum worst-case drift specification of 10 ppm/°C. This internal reference is useful as it requires no additional cost to use it as long as the drift specification is low enough for the given application. Otherwise, you can always use an external reference while still retaining this option with the DAC81404 for even higher-accuracy applications.
Specification No. 3: DC accuracy (TUE)
A common specification used to characterize most precision DACs is the total unadjusted error (TUE), represented by the root-sum-square of the relative accuracy or integral nonlinearity (INL), the offset error, and the gain error of the DAC.
TUE is the best way to combine all of the major DC errors of the DAC and represents an overall specification to define how accurate a DAC is. Advanced DACs like the DAC81404 boast an extremely low TUE of 0.05% maximum full-scale range. A low TUE is important because the DAC needs to hold a particular value over time and across temperature. This stability is important for programmable reference applications.
Bonus feature: programmability
Why is programmability so important in a reference? What problems does it solve vs. a fixed reference? First, programmable references provide flexibility – particularly the flexibility to compensate the output over time to adjust for environmental changes or system requirements. They also give you the ability to calibrate the output to systems as they are built in the factory flow. A DAC’s output is controllable via digital inputs. You can set the DAC output to any value necessary to replace a reference.