An LED filament light bulb is an electric light bulb which produces light with an LED that is shaped to look like the filament of an incandescent light bulb. The light bulb is supplied with electric current by feed-through terminals or wires embedded in the glass.
An LED filament type design light bulb was first produced by Ushio Lighting in 2008, intended to mimic the appearance of a standard Edison light bulb.
- The most common use of filament style lamps is in retro lamps, i.e., clear glass lamps that allow the “filaments” to be seen.
The LED filament bulb market size is expected to approximately reach 300 million bulbs by 2017 and double to 600 million bulbs by 2018 (Epistar Market Analysis Report) and has immense potential in the LED lighting market.
The LED filament bulb has become popular in the lighting market mainly because major buyers and consumers in decorative lighting, art lamps, chandeliers and classical luminaires were gradually replacing conventional light sources, including filament bulbs and halogen light sources with LED lights. Previously, traditional LED bulbs failed to meet the aesthetic demands of traditional luminaire manufacturers, which paved the way to LED filaments emergence on the market.
Currently, LED filaments are mainly applied in A19, A60 and A55 products. Bulb specifications are mainly centered on 450 lm bulbs that use four LED filaments designed to meet B35 and F35 specs, for 250 lm LED candle lights the design uses two filaments. In the application sector, the LED filament bulbs are applied in vintage bulbs, candle lights, light bulbs, and decorative lights for existing and replacement demands.
Epistar also projects LED filament bulbs will encounter the same price plunge issues as LED bulbs, which will also propel the product’s market penetration.
Ideal applications of LED Filament bulbs include Hotel & Restaurant Lighting, Residential Lighting, Retail Lighting and Accent Lighting
Manufacturers are placing more emphasis on LED filament bulbs patents because one of the crucial LED filament technologies involves adhering several LED chips onto a transparent substrate to emit a better light shape and can improve luminous efficacy.
The Technology of LED Filaments
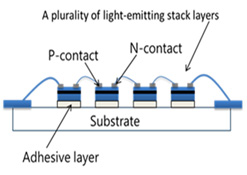 One of the advantages of filaments is that the LEDs can be configured for omni-directional light, the same as an incandescent lamp. The 360 degrees flux geometry has been missing in most LED lamps available in the market today.
One of the advantages of filaments is that the LEDs can be configured for omni-directional light, the same as an incandescent lamp. The 360 degrees flux geometry has been missing in most LED lamps available in the market today.
LED filaments lead to higher efficiencies through the use of more LED emitters from lower driving currents. LED Filaments are upto 40% more efficient than traditional LED solutions and can provide efficacy of 150lm/W.
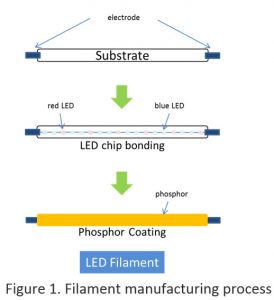 Besides being Environmentally Friendly (Mercury Free, Lead Free & RoHS Compliant), LED Filament bulbs are also Application Friendly (UV Free & IR Free). Most LED Filament bulbs are dimmable and Omni Directional.
Besides being Environmentally Friendly (Mercury Free, Lead Free & RoHS Compliant), LED Filament bulbs are also Application Friendly (UV Free & IR Free). Most LED Filament bulbs are dimmable and Omni Directional.
The LED filament is composed of a series of LEDs on a transparent substrate, referred to as Chip-On-Glass (COG). The substrate transparency allows the emitted light to disperse evenly and uniformly without any interference. An even coating of phosphor in a silicone resin binder material converts the blue light generated by the LEDs into a mixture of red, blue, and green light to create a specified light temperature.
 The LED filament can be made with sapphire, glass, and transparent ceramic substrates. Metal substrate LED filaments are rarely seen on the market. Even though glass substrates are less costly, the filament has very low thermal dissipation. Filament bulb designs are therefore restricted by glass filament’s thickness of 1 mm to 2 mm. In comparison, sapphire substrates are thinner with a substrate thickness of 0.8 mm to 1 mm. Moreover, its quality matches transparent ceramic substrates, yet it is still slightly more costly than glass. Sapphire substrate’s comprehensive supply chain has made it the most prominent filament material found in LED filament bulbs, taking up 70% to 80% market share. Trailing in second is transparent ceramic substrate filaments 20% market share, followed by glass filaments mere 10%.
The LED filament can be made with sapphire, glass, and transparent ceramic substrates. Metal substrate LED filaments are rarely seen on the market. Even though glass substrates are less costly, the filament has very low thermal dissipation. Filament bulb designs are therefore restricted by glass filament’s thickness of 1 mm to 2 mm. In comparison, sapphire substrates are thinner with a substrate thickness of 0.8 mm to 1 mm. Moreover, its quality matches transparent ceramic substrates, yet it is still slightly more costly than glass. Sapphire substrate’s comprehensive supply chain has made it the most prominent filament material found in LED filament bulbs, taking up 70% to 80% market share. Trailing in second is transparent ceramic substrate filaments 20% market share, followed by glass filaments mere 10%.
The LED filament is then encapsulated in a resin made up of a silicone and phosphor mixture that transforms the LED chips’ blue light into white light. This design allows the use both of both blue LEDs as well as red LEDs to modulate the color temperature. Most manufacturers rely solely on the phosphor to set the color temperature.
Filament LED designs achieves even better  performance than their traditional LED lamp counterparts by under driving much smaller, low-power LED chips. The result is less heat, better efficacies, and sleeker designs with no heat sink needed.
performance than their traditional LED lamp counterparts by under driving much smaller, low-power LED chips. The result is less heat, better efficacies, and sleeker designs with no heat sink needed.
The high voltage-low current scheme is an ideal combination for controlling the heat.
 One of the novel approaches to thermal management is to use a special gas mixture inside the glass lamp to facilitate the heat transfer to the glass surface more efficiently.
One of the novel approaches to thermal management is to use a special gas mixture inside the glass lamp to facilitate the heat transfer to the glass surface more efficiently.
MLS is a significant player in the LED Filaments business with dedicated manufacturing facility for Filament Bulbs in China. We are supplying LED Filaments as well as Private Branded bulbs to multiple customers across the world and are upgrading our manufacturing facilities for larger production capabilities.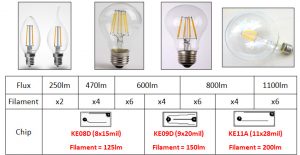
Conclusion
With aesthetic appeal and significant performance advantages, LED filament bulbs represent a flawless intersection of form and function — vintage look and advanced engineering. Coupled with the market projections for the coming years, LED Filament Bulbs are surely the next generation in the evolution of LED Lighting.
– Krishan Sujan, COO, MLS India Pvt. Ltd.









